Fig. 2.
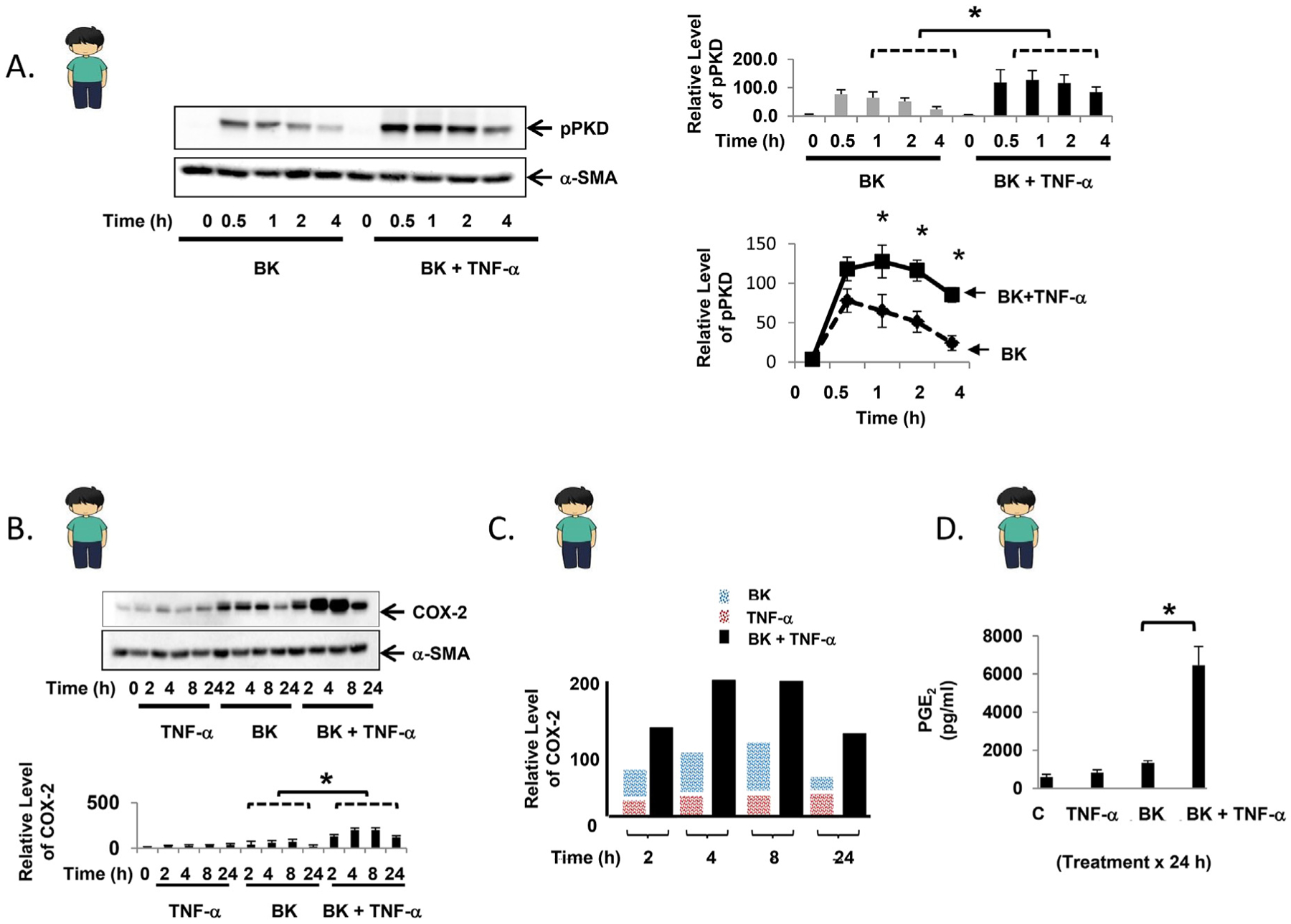
TNF-α enhances bradykinin-mediated PKD phosphorylation and leads to synergistic COX-2 expression in primary human myofibroblasts. A. Confluent primary human myofibroblasts were equilibrated in serum-free media for 30min and exposed to BK (100 nM) ± TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for up to 4h. Results are shown graphically as the mean ± S.E. n ≥ 3, expressed as the relative expression level of pPKD. B. Confluent primary human myofibroblasts were equilibrated in serum-free media for 30min and exposed to TNF-α (10 ng/ml) ± BK (100 nM) for up to 24h. The results are shown graphically as the mean ± S.E. n ≥ 3, expressed as the relative expression level of COX-2. C. Graphical representation of COX-2 protein expression induced by BK alone (blue bar), TNF-α alone (red bar), or the combination (black bar) over 24h. D. Following exposure of confluent primary human myofibroblasts to TNF-α (10 ng/ml) ± BK (100 nM) for 24h, PGE2 concentration was quantified from cell culture supernatant by ELISA. Control: 598.0 ± 131.1 pg/ml, TNF-α: 841.7 ± 135.4 pg/ml, BK: 1340.3 ± 120.8 pg/ml, TNF-α + BK: 6462.2 ± 989.4 pg/ml * denotes p < 0.05. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)
