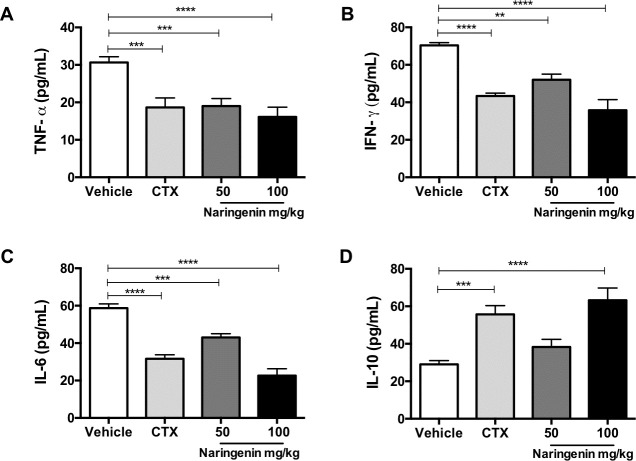
Fig 3. Naringenin reduced the serum concentration of proinflammatory cytokines and increased the concentration of IL-10.
Previous to sacrifice, serum was obtained from each mouse by blood sampling of the submandibular vein. The cytokines concentration from each serum sample was measured by ELISA assay. Naringenin reduced the serum concentration of proinflammatory cytokines as (A) TNF-α, (B) IFN- γ, (C) IL-6. Conversely, Naringenin at a dose of 100 mg/kg significantly increased the serum concentration of (D) IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine. Statistical analysis was carried out by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test and data presented as mean ± SD, n ≥ 5. ** p≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001 compared versus vehicle.