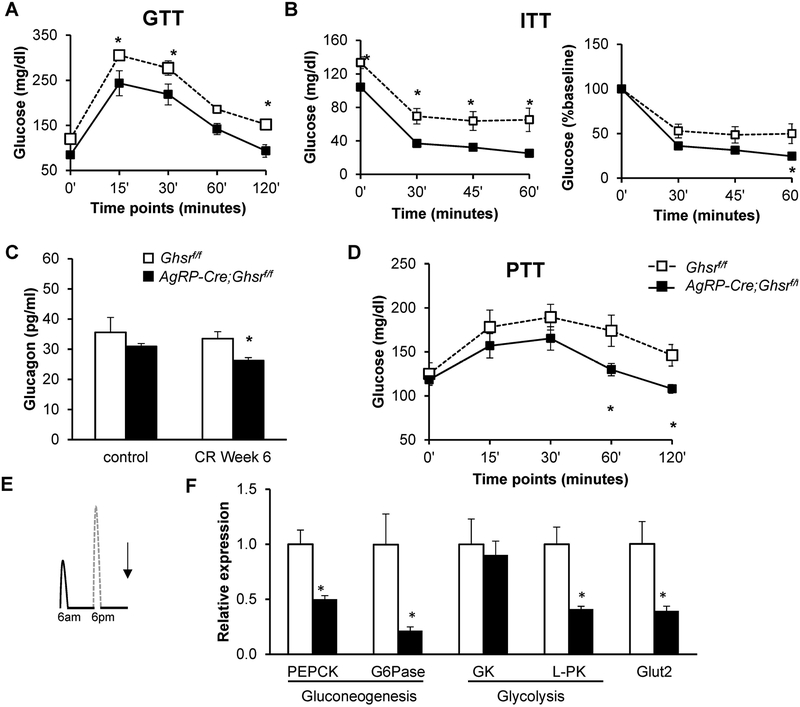
Figure 4. GHS-R deletion in AgRP neurons increases insulin sensitivity and decreases hepatic glucose production under calorie restriction.
(A) Glucose levels during GTT after 18 hours overnight fast; (B) Glucose levels during ITT after 3 hours morning fast with glucose levels (left) and percentage of glucose change from baseline (right); (C) Plasma glucagon levels; (D) Glucose levels during PTT after 18 hours overnight fast that had been on 11 weeks of CR. Mice from Cohort 2 were used in the in vivo experiments for GTT, ITT and PTT, n = 8 for each group. (E) Diagram depicting the time at which liver tissues were collected for gene expression analysis, Cohort 1; (F) Expression of genes involved in hepatic glucose production. Tissues from Cohort 1, collected as indicated in E, were analyzed, n =5 for each group. Data in A, B, and D were analyzed with two-way ANOVA with repeated measures (Time and Genotype), followed by Šidák’s post hoc analysis. Data in C were analyzed with two-way ANOVA (Diet and Genotype), followed by Šidák’s post hoc analysis. Data in F were analyzed with Holm-Šidák method with correction for multiple t-tests. * p < 0.05, Ghsrf/f vs. AgRP-Cre;Ghsrf/f.