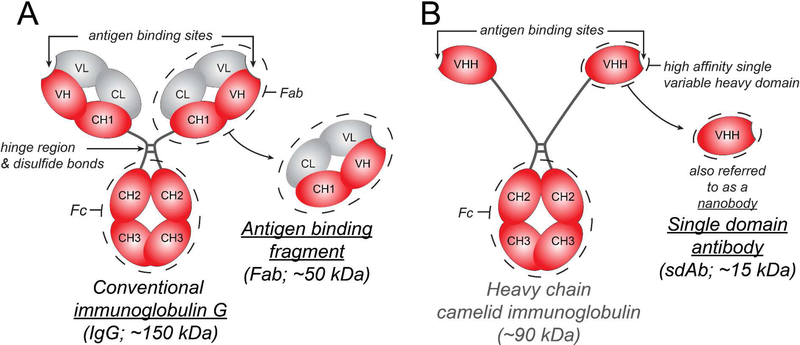
Figure 1.
Summary of IgG, Fab, and sdAb structure and sizes. (A) Full length IgG is a Y shaped molecule made up of four polypeptide chains – two heavy chains (red) and two light chains (grey) that are linked by disulfide bonds. Each polypeptide chain has constant domains (C) and variable domains (V). There are two Fab arms, each containing an antigen-binding site made up of the variable domains of the heavy and light chains, which can recognize antigens with high specificity. The crystallizable fragment or Fc arm can interact with Fc receptors. (B) Camelids, sharks and other cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) produce a unique IgG molecule consisting of heavy chains alone. A camelid IgG molecule is depicted here. A single heavy chain variable domain is also referred to as a single domain antibody or nanobody. Unlike the antibody variable domains in other species, camelid and cartilaginous fish variable domains do not aggregate when isolated and retain their antigen binding capacity; this has generated interest in their use as therapeutics when a smaller size and no Fc interactions are desired 10.