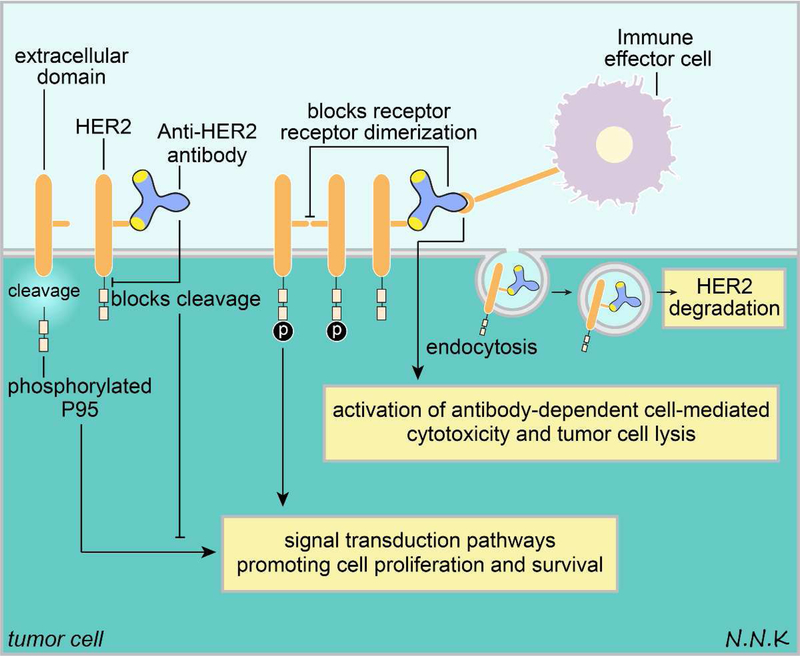
Figure 7. Passive immunotherapy strategy to treat breast cancer brain metastases using anti-HER2 antibodies.
HER2 overexpressing breast cancer brain metastases may be treated with anti-HER2 antibodies. Anti-HER2 passive immunotherapy may have several effects. First, HER2 homo or hetero dimerization that drives downstream signaling that promotes tumor cell survival may be disrupted using anti-HER2 antibodies. Second, the extracellular domain of HER2 is typically shed in tumor cells, leaving behind a phosphorylated P95 that is membrane bound and can drive downstream signaling promoting tumor cell growth and survival; anti-HER2 antibodies can bind to the HER2 extracellular domain and prevent its cleavage. Third, anti-HER2 antibodies may bind to HER2 expressed on tumor cell surfaces and initiate an Fc-mediated immune effector function that targets tumor cells. Fourth and finally, anti-HER2 antibodies may bind to HER2 and cause its internalization by endocytosis, resulting in HER2 degradation. Adapted from: 91. Abbreviations: HER2 – human epidermal growth factor receptor 2.