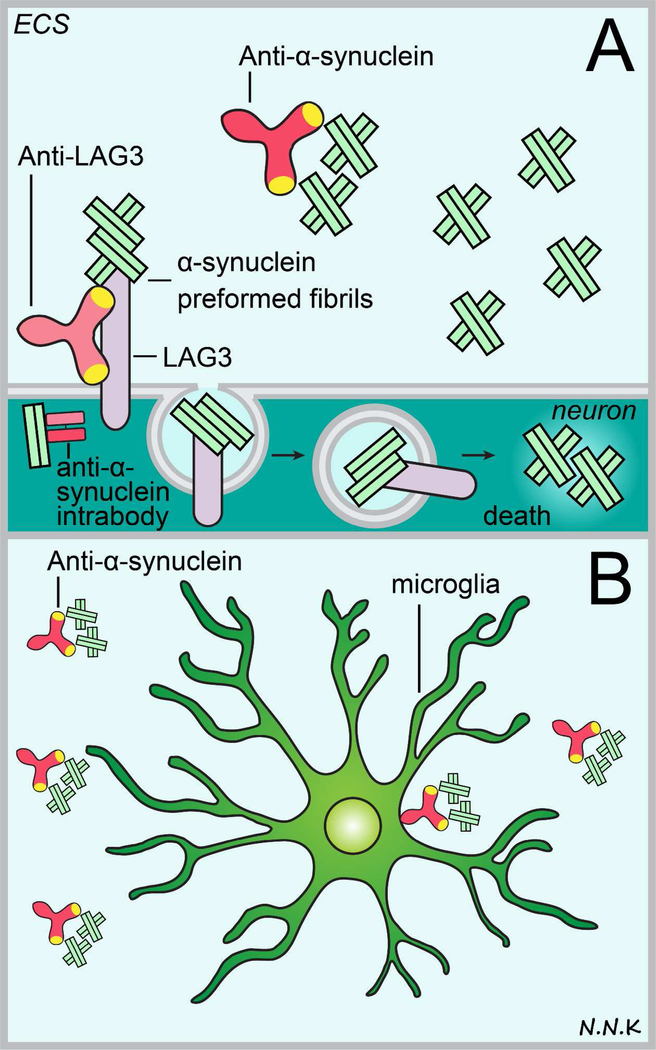
Figure 9. Passive immunotherapy strategies to treat Parkinson’s disease.
Disease pathology in Parkinson’s disease typically entails the accumulation and aggregation of abnormal alpha synuclein protein, subsequently leading to neuronal cell death and cognitive decline. Anti-alpha synuclein antibodies may be used to block the intracellular aggregation of abnormal alpha synuclein which typically leads to the formation of intracellular Lewy bodies (thus the most likely strategy would be to use intrabodies) or prevent the cell-to-cell transmission of extracellular abnormal alpha synuclein (using conventional antibodies). Extracellular anti-alpha synuclein antibodies may prevent abnormal alpha synuclein monomers and oligomers from aggregating further and may recruit microglia to phagocytose abnormal protein via Fc mediated interactions. Lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3) protein was recently implicated in the internalization of pathologic alpha synuclein during cell-to-cell transmission so an anti-LAG3 antibody strategy may therefore be promising to prevent the spread of alpha synuclein pathology. Abbreviations: ECS – extracellular space. Adapted from: 217,231.