Figure 1).
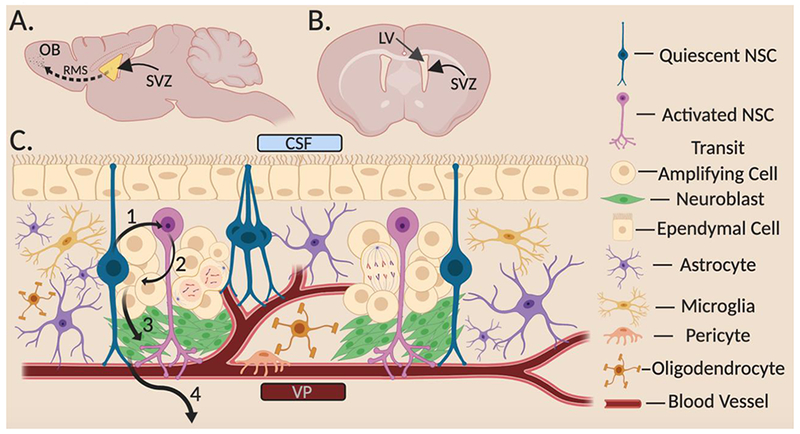
The young SVZ Structure and Organization A) Sagittal section of murine brain showing lateral SVZ enface with the rostral migratory stream (RMS). B) Coronal section of murine brain showing the LV adjacent to lateral SVZ. C) Cellular SVZ niche cross section. The SVZ lies between the CSF (top) and VP (bottom). qNSCs make contact through the ependymal layer and receive signals from the CSF. Upon activation, qNSCs transition to aNSCs (1) where they either divide symmetrically or asymmetrically into TACs (2). TACs then produce NBs (3) that then exit the SVZ (4) and migrate along the RMS to the OB where they will terminally differentiation into inhibitory neurons. qNSC, quiescent neural stem cell; aNSC, active neural stem cell; TAC, transit amplifying cell; NB, neuroblast; OB, olfactory bulb; RMS, rostral migratory stream; LV, lateral ventricle; SVZ, subventricular zone; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; VP, vascular plexus.
