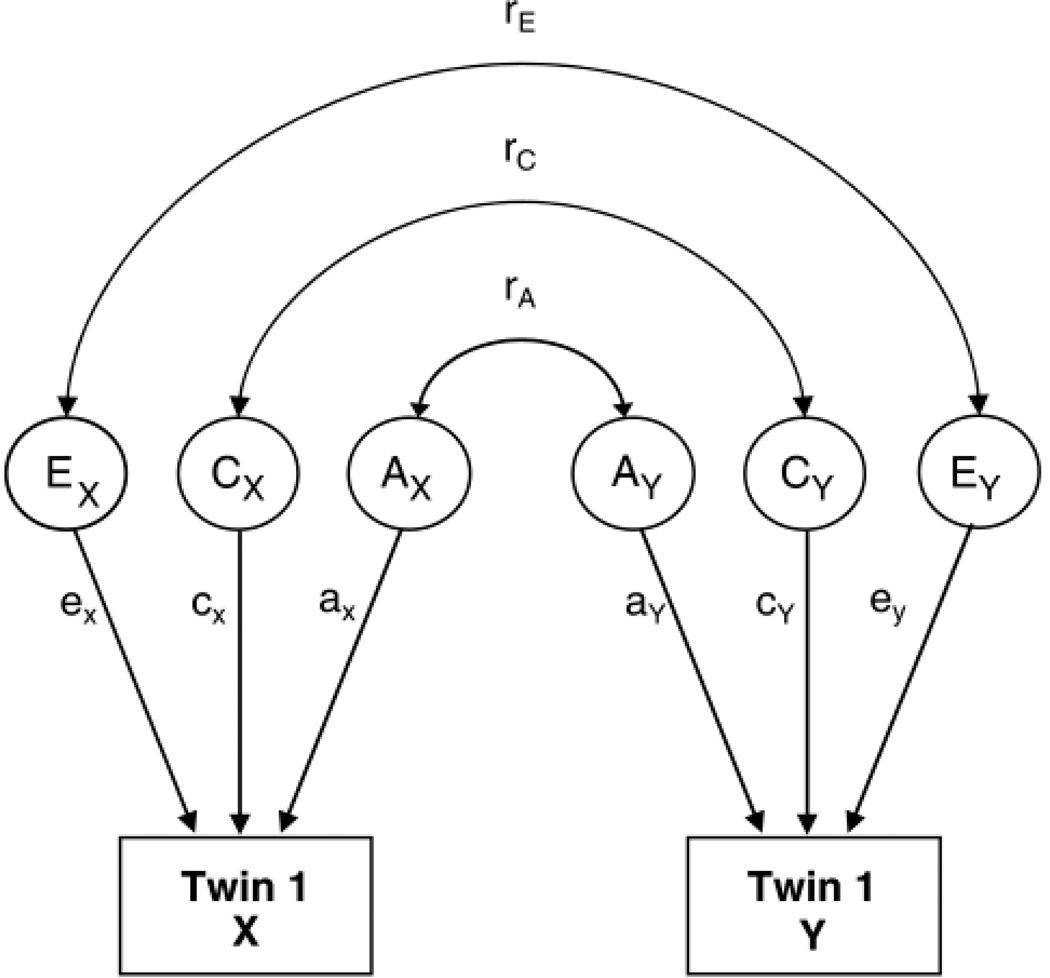
Figure 1:
Path diagram of a bivariate correlated factors model
Note: In a univariate model, the variance in the phenotype is parsed into that which is due to additive genetic effects (A), shared environmental effects (C), and non-shared environmental effects (E). In the bivariate correlated factors model, the shared sources of variance between two phenotypes (X and Y) are decomposed into a genetic correlation (RA), a shared environment correlation (RC), and a non-shared environment correlation (RE).