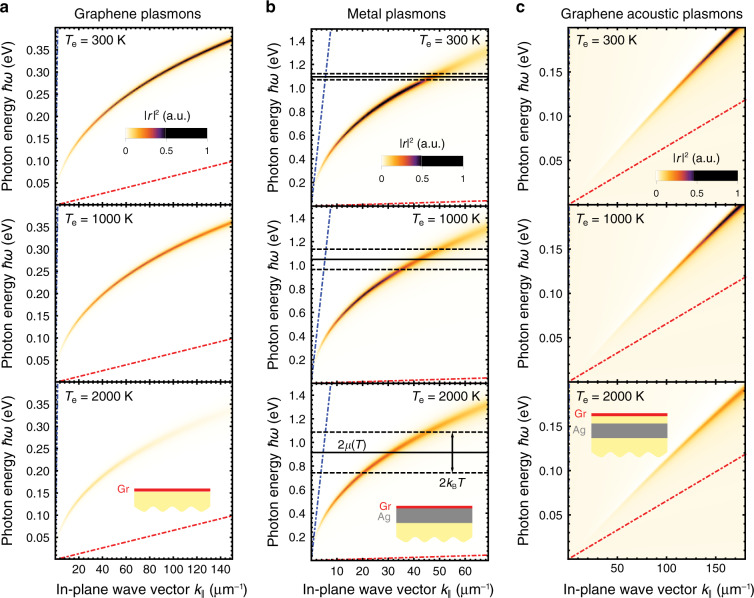
Fig. 2. Temperature dependence of the plasmon dispersion relation.
We plot the squared Fresnel reflection coefficient for p polarization as a function of the photon energy ħω and in-plane wave vector for three different configurations: a graphene, b graphene/silver and c graphene/spacer/silver films, all of which are supported on a dielectric substrate (ε = 2), as shown in the lower insets. The silver layer thickness is 1 nm in b and 2 nm in c (i.e., approximately 4 and 8 (111) atomic layers, respectively42). The spacer in c has ε = 2 and 1-nm thickness. We consider three different values of the electron temperature Te in graphene (top to bottom, see labels), while the metal electrons and the lattices of all materials are kept at room temperature T0 = 300 K. Graphene is doped to EF = 0.55 eV in all cases. Light (, blue) and Fermi (, red) lines are shown for reference