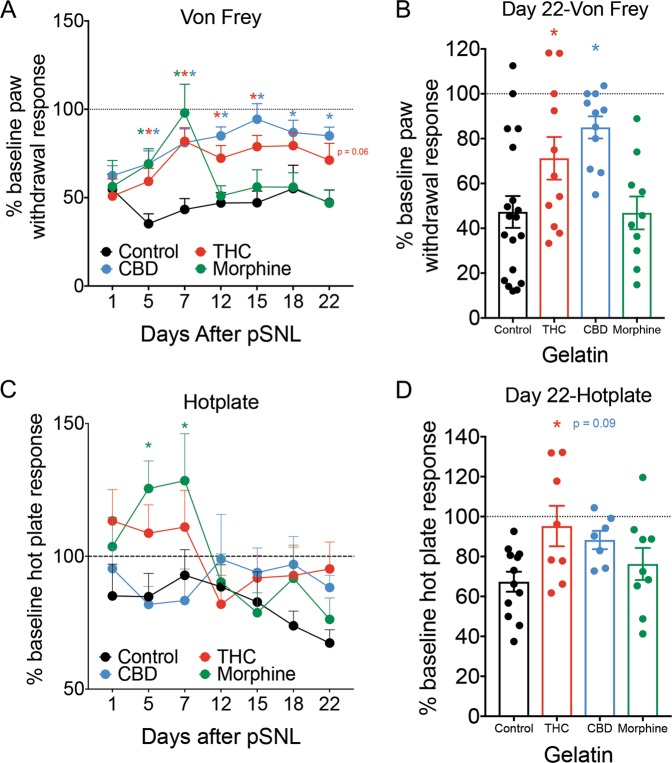
Fig. 3. Cannabinoid consumption decreases measurements of neuropathic pain over 3 weeks.
a Paw withdrawal thresholds, plotted as a percentage of pre-pSNL response, are shown 1 day after pSNL, and on the 6 subsequent testing days after introduction of either control, THC, CBD, or morphine gelatin. THC and CBD groups showed long-lasting reduction in allodynia, while the effect of morphine lasted approximately 1 week (n = 10–19 per group). b Comparison of percentage of pre-pSNL response on day 22, the final day of pain testing, between the 4 treatment groups (n = 10–19 per group). c Latency to respond to hot plate, plotted as a percentage of pre-pSNL response, are shown 1 day after pSNL, and on the 6 subsequent testing days after introduction of either control, THC, CBD, or morphine gelatin. The morphine group showed an analgesic response in the first week, while no other groups were significantly different from control (n = 7–12 per group). d Comparison of percentage of pre-pSNL response on day 22. THC significantly reduced hyperalgesia while there was a trend effect of CBD (n = 7–12 per group). *p < 0.05, data represent the mean ± SEM.