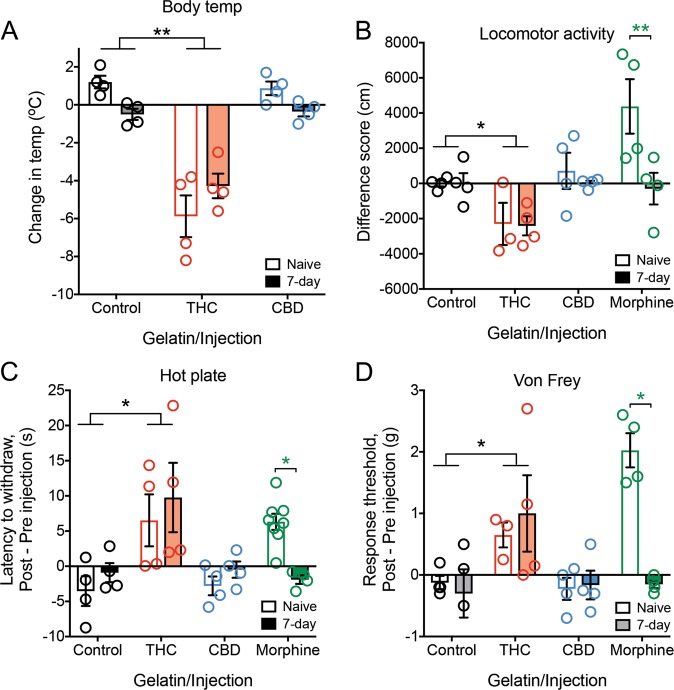
Fig. 4. Measures of analgesia and body temperature in neuropathic pain-naïve mice.
a Change in body temperature 2 h after either vehicle, THC (30 mg/kg i.p.), or CBD (30 mg/kg i.p.) experimenter-administered dose in 7-day gelatin consuming animals or drug-naïve controls. THC injected mice showed the predicted decrease in body temperature in both groups, whereas CBD showed no change (n = 4 per group). b Change in locomotor activity after either vehicle, THC (30 mg/kg i.p.), CBD (30 mg/kg i.p.), or morphine (10 mg/kg i.p.) experimenter-administered dose in 7-day gelatin consuming animals or drug-naïve controls (n = 3–4 per group). c Change in latency to pain response 2 h after either vehicle, THC (30 mg/kg i.p.), CBD (30 mg/kg i.p.), or 30 min after morphine (10 mg/kg i.p.) experimenter-administered dose in 7-day gelatin consuming animals or drug-naïve controls. THC injected mice in both groups showed a similar increase in analgesic response, while CBD animals showed no change. Drug-naïve morphine injected animals showed analgesia, while there was no change in mice that have consumed morphine for 7 days (n = 4–8 per group). d Change in paw withdrawal threshold 2 h after either vehicle, THC (30 mg/kg i.p.), CBD (30 mg/kg i.p.), or 30 min after morphine (10 mg/kg i.p.) experimenter-administered dose in 7-day gelatin consuming animals or drug-naïve controls. THC injected mice in both groups showed a similar increase in paw withdrawal threshold, while CBD animals again showed no change. Drug-naïve morphine injected animals showed an increase in paw withdrawal threshold, while there was no change in mice that have consumed morphine for 7 days (n = 3–4 per group). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, data represent the mean ± SEM.