Figure 3.
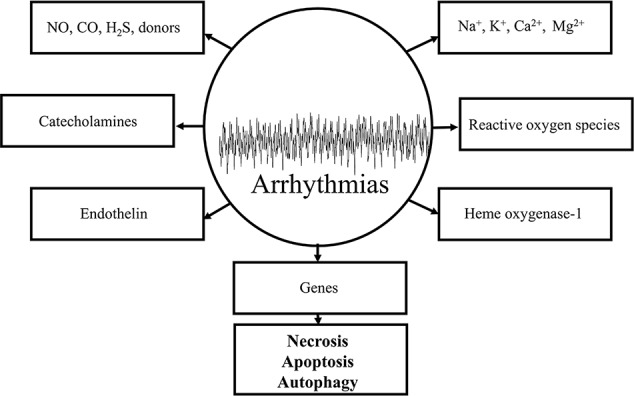
Schematic representation of some important arrhythmogenic components and mediators in the genesis of reperfusion-induced arrhythmias. All of the depicted mechanisms are very complex and each of them significantly contributes to the maldistribution of Na+, K+, Ca2+ exchange mechanisms by virtue of causing damages in cell membranes and receptors leading to necrotic-, apoptotic-, and autophagic-induced cell deaths.
