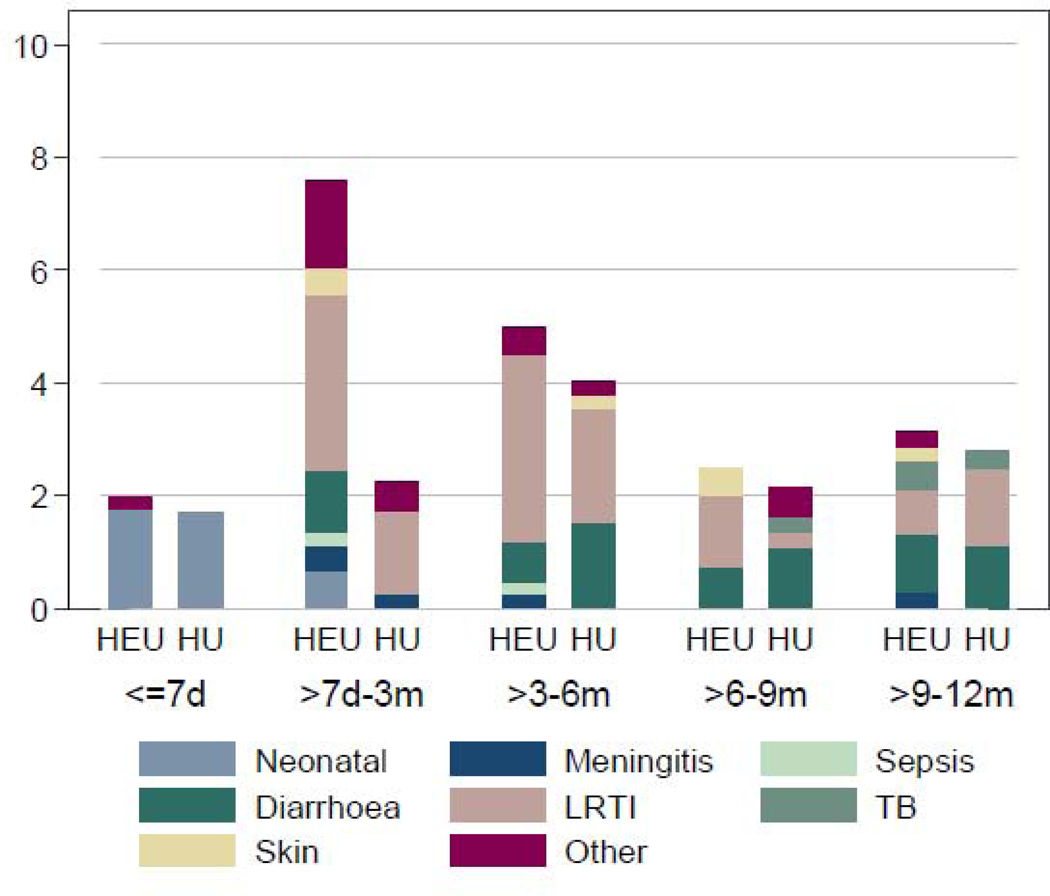
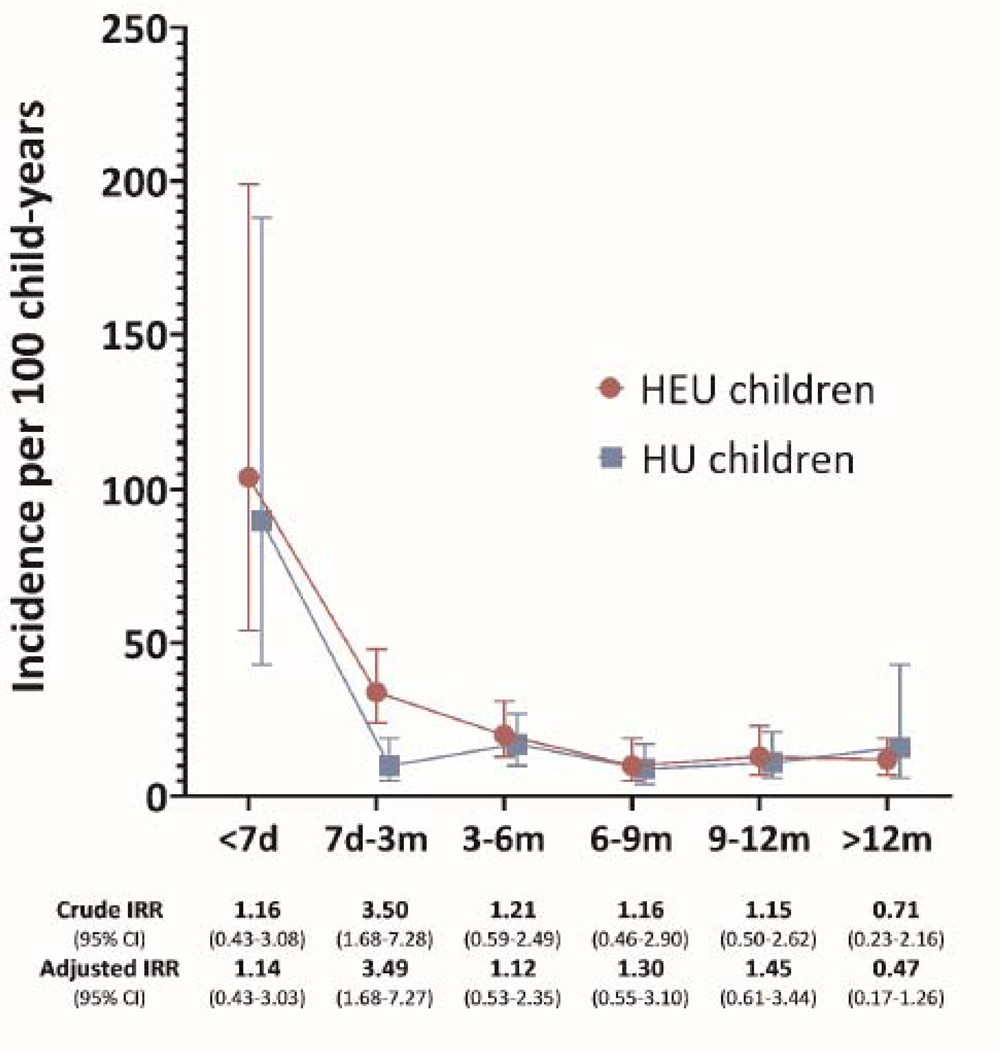
FIGURE 2.
Infection-related hospitalizations comparing HIV-exposed uninfected and HIV-unexposed children over time: distribution of diagnoses and incidence over time
2A. Infection-related causes for hospitalization: distribution by HIV exposure and age category
Legend: HEU, HIV-exposed uninfected; HU, HIV-unexposed uninfected; d, days; m, months; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection (includes pneumonia and bronchiolitis); TB, pulmonary tuberculosis; Percentages based on number of admissions divided by number of children in category
2B.Infection-related hospitalization: incidence rates and rate ratios comoaring HIV-exposed uninfected to HIV-unexposed children over time
Legend: HEU, HIV-exposed uninfected children; HU, HIV-unexposed chidren; d, days; m, months; IRR, incidence rate ratio from Poisson regression models adjusted for clustering; Cl, confidence internal. Muitivariable models adjusted for socio-economic factors (access to flush toilet and running water inside the home). maternal depression, preterm birth, child underweight, vaccination status. quality of breastfeeding and season at birth
Sampie size per age internal: <7 days, N=869; 7 days-3 months, N=849; 3–6 months, N=808; 6–9 months, N=782; 9–12 months, N=745; >12 months, N=664