FIGURE 1.
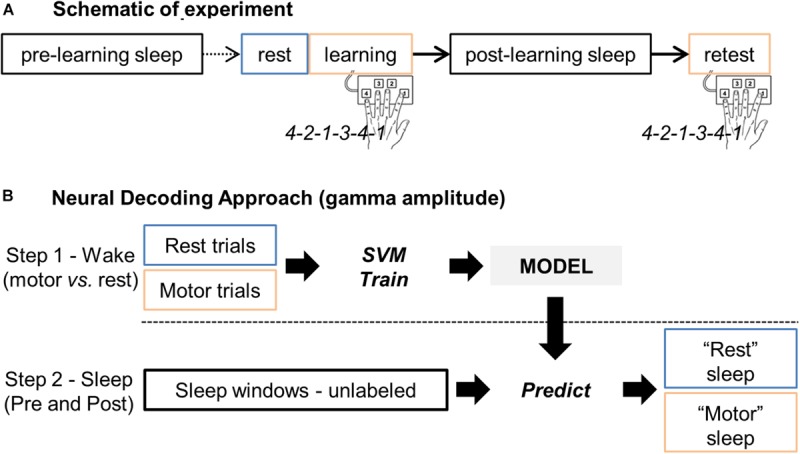
(A) Schematic representation of the experiment, including the rest, learning and retest sessions, and the two sleep periods before (pre-learning sleep or “sleepPre”) and after (post-learning sleep or “sleepPost”) learning, respectively. (B) Main steps of the neural decoding approach. Gamma band activity during rest and finger tapping were first used as features (i.e. predictors) to train a support vector machine (SVM) model for two-class classification i.e. “motor” vs. “rest” classes. The trained model was then applied to the unlabeled sleep samples: the gamma band activity during sleep was processed by the model to return for each windowed sleep trial a class label (motor- or rest-vote). Finally, the proportion of sleep windows classified as “motor” (i.e. the proportion of motor-votes) was compared between the two sleep periods (sleepPre vs. sleepPost).
