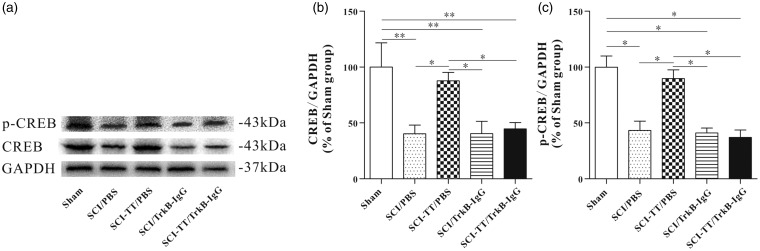
Figure 3.
Effect of BWSTT on CREB and p-CREB synthesis in the distal spinal cord of SCI rats with or without blocking TrkB signaling. (a) Western blot image of CREB and p-CREB in the Sham group, the SCI/PBS group, the SCI-TT/PBS group, the SCI/TrkB-IgG group, and the SCI-TT/TrkB-IgG group at the end of the experiment. (b) The statistical graph of the relative density of CREB. (c) The statistical graph of the relative density of p-CREB. n = 4 rats per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by the LSD or Bonferroni test.
BWSTT: body weight-supported treadmill training; TT: treadmill training; SCI: spinal cord injury; PBS: phosphate-buffered saline; TrkB: tropomyosin-related kinase B; CREB: cAMP-response element binding protein; p-CREB: Phospho-CREB; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ANOVA: analysis of variance.