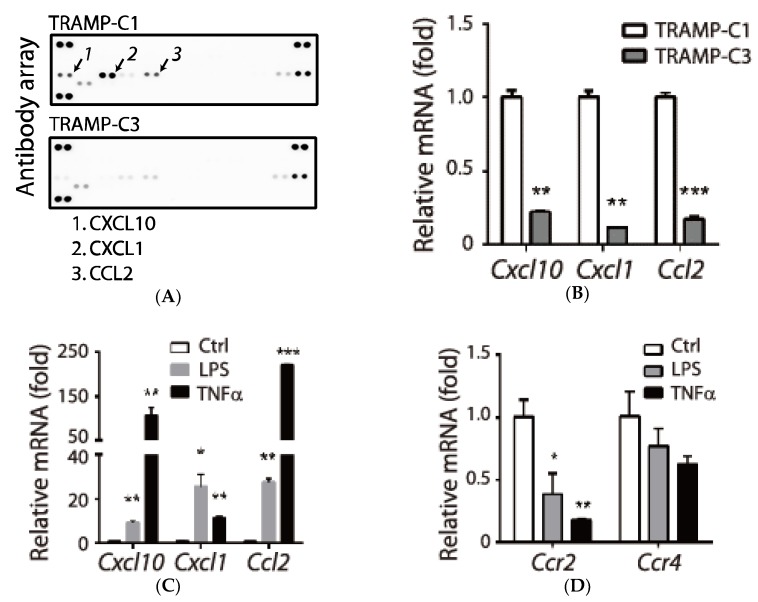
Figure 1.
Association of pro-inflammatory chemokines with the tumorigenic prostate cancer cell line transgenic adenocarcinoma mouse prostate (TRAMP)-C1. (A) Identification of tumor-associated chemokines (arrows) by comparing conditioned media prepared from TRAMP-C1 and non-tumorigenic TRAMP-C3 cells using an antibody array. Reference spots at the corners, except for the bottom-right one, served as quality control. Induced genes in TRAMP-C1 are labeled with numbers. (B) Relative mRNA levels between TRAMP-C1 and TRAMP-C3 cells were determined by a real-time qPCR. (C) Induction of tumor-associated cytokines by inflammatory signals. TRAMP-C1 cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/mL) or mouse tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα, 10 ng/mL) for 6 h followed by mRNA purification and a real-time qPCR analysis. (D) Suppression of Ccr2 expression by inflammatory signals. Samples from panel C were analyzed using primers against Ccr2 and Ccr4 by a qPCR. Control: vehicle treatment. qPCR measurements were derived from three technical replicates and results are presented as the mean ± SD. Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.