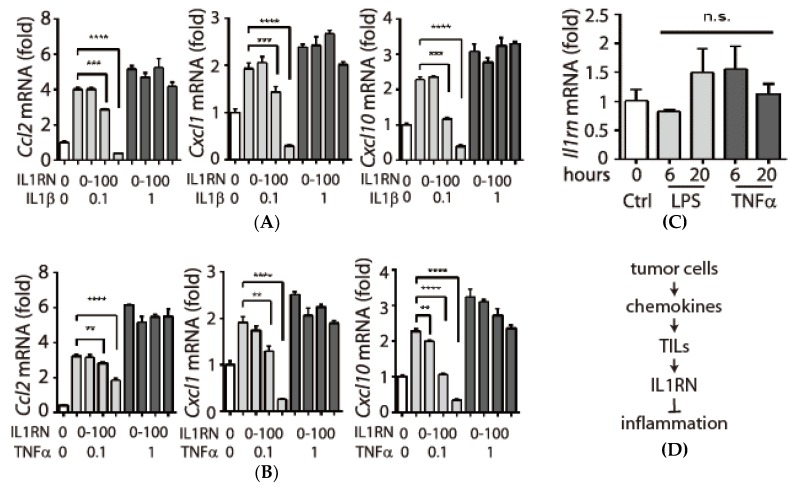
Figure 5.
Inhibitory effects of interleukin-1 (IL1) receptor antagonist (IL1RN) to pro-inflammatory cytokines. (A) Monitoring inhibitory effects of IL1RN on IL1β. Different concentrations of IL1RN proteins (0, 1, 10, and 100 ng/mL, labeled as a triangle) were mixed with a fixed dosage of IL1β (0.1 or 1 ng/mL) in TRAMP-C1 cells for 6 h. Relative mRNA levels were measured by primers targeting Ccl2 (left), Cxcl1 (middle), and Cxcl10 (right). (B) Monitoring inhibitory effects of IL1RN on TNFα (0.1 or 1 ng/mL). (C) Il1rn mRNA was not affected by inflammatory signaling. TRAMP-C1 cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/mL) or mouse tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα, 10 ng/mL) for 6 or 20 h followed by mRNA purification and a real-time qPCR analysis. qPCR measurements were derived from three replicates and results are presented as the mean ± SD. Student’s t-test. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (D) A working model depicts the recruitment of TILs by tumor-associated pro-inflammatory chemokines (e.g., CCL2). The recruited TILs secret IL1RN which suppresses inflammatory signals by IL1RN-mediated functions in tumor microenvironment.