Figure. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Features of Some Patients.
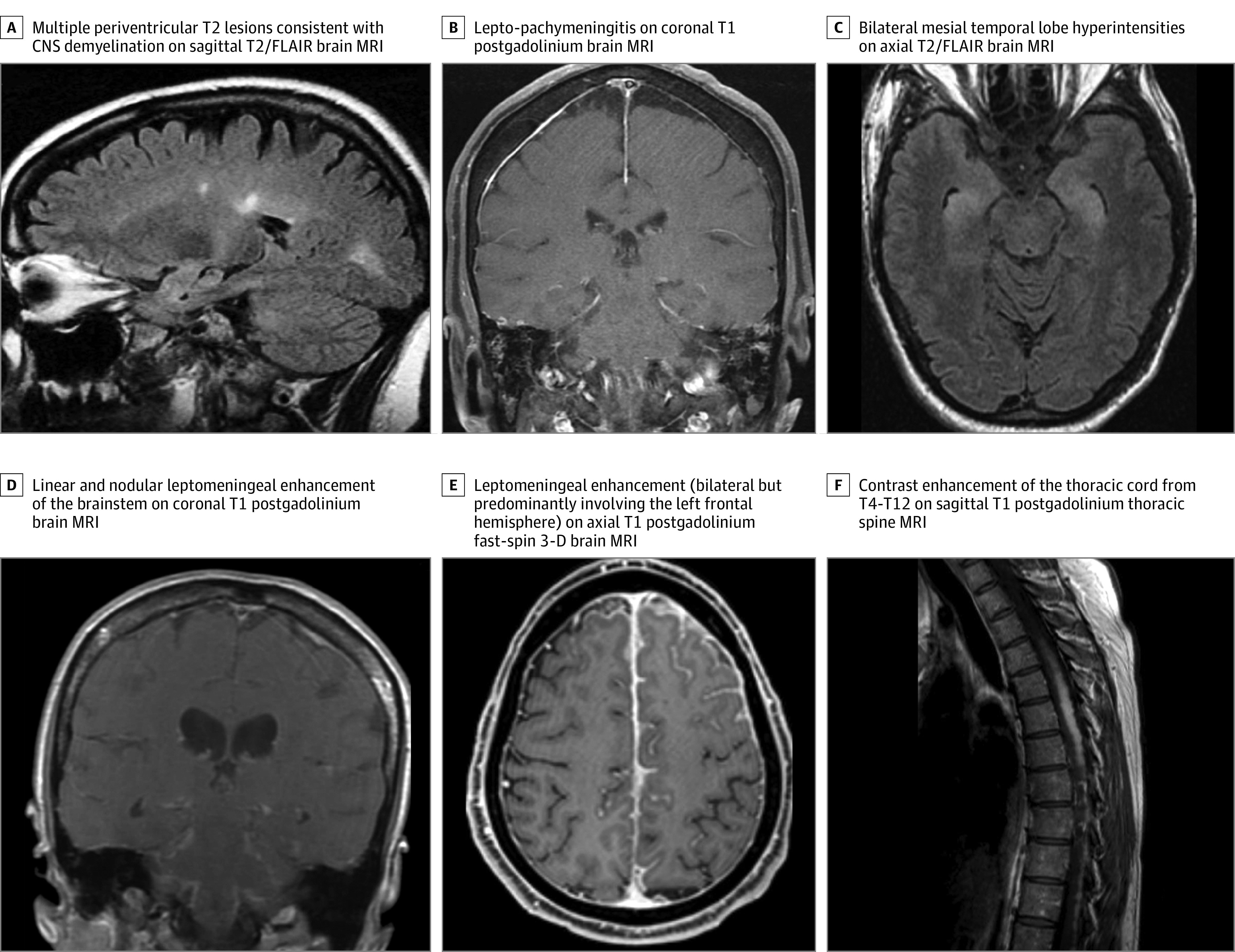
A, A patient with Crohn disease for 3 years who was treated with adalimumab for 10 years presented with a thoracic sensory band and lower-limb paresthesia. The patient had a cervical spine MRI that revealed multiple short-segment T2 hyperintense lesions with contrast enhancement. The diagnosis was central nervous system (CNS) demyelination. B, A patient with a history of rheumatoid arthritis who was treated with adalimumab for 16 years presented with headaches and a generalized tonic-clonic seizure; an infectious and malignant neoplasm evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) had a negative result. Dural biopsy results revealed necrotizing meningitis, and were negative for special stains for microorganisms, including mycobacteria and fungi. The diagnosis was idiopathic lepto-pachymeningitis. C, A patient with ankylosing spondylitis and type 1 diabetes was treated with several tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors for a cumulative total of 2 years (infliximab twice, etanercept, and adalimumab). The patient had ceased using TNF inhibitor 10 months before presenting with acute confusion. The CSF analysis and positron emission tomography (PET) scan had a negative result for neural antibodies and malignant neoplasm. Serum autoimmune neural antibodies had a positive result (serum acetylcholine receptor modulating antibody, 34% loss; GAD65 antibody, 0.35 nmol/L; striational antibody, 1:240). The diagnosis was autoimmune encephalitis. The patient had a clinically robust response to intravenous methylprednisolone acetate. D, A patient with Crohn disease for 10 years was treated with adalimumab for 6 months, then infliximab for 6 months before presenting with new-onset headaches, hearing loss, paresthesias, left facial droop, numbness and diplopia. In addition to a brain MRI scan showing leptomeningeal enhancement of the brainstem, an MRI of the cervical and thoracic spine also revealed patchy leptomeningeal enhancement of the spinal cord. Results of an infectious and neoplastic evaluation of the CSF were negative. A PET scan identified increased fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake in the mediastinum, and a biopsy of subcarinal lymph node confirmed granulomatous disease. Special stains for microorganisms, including mycobacteria and fungi, had a negative result. The diagnosis was neurosarcoidosis. E, A patient with rheumatoid arthritis for 8 years who was treated with etanercept and methotrexate sodium presented with new-onset headaches and paresthesia of the right face and limbs. A right frontal biopsy specimen demonstrated necrotizing granulomatous inflammation that extensively involved the leptomeninges. Special stains for microorganisms, including mycobacteria and fungi, had a negative result. The diagnosis was neurosarcoidosis. F, A patient with a history of Crohn disease who was treated with infliximab for 3 years presented with myelopathic symptoms. A PET scan showed moderately intense FDG activity in the thoracic spinal cord. A thoracic cord biopsy demonstrated necrotizing granulomatous inflammation. Special stains for microorganisms, including mycobacteria and fungi, had a negative result. The diagnosis was neurosarcoidosis. FLAIR indicates fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence.
