Figure 2. The LDAF1-seipin complex defines LD formation sites.
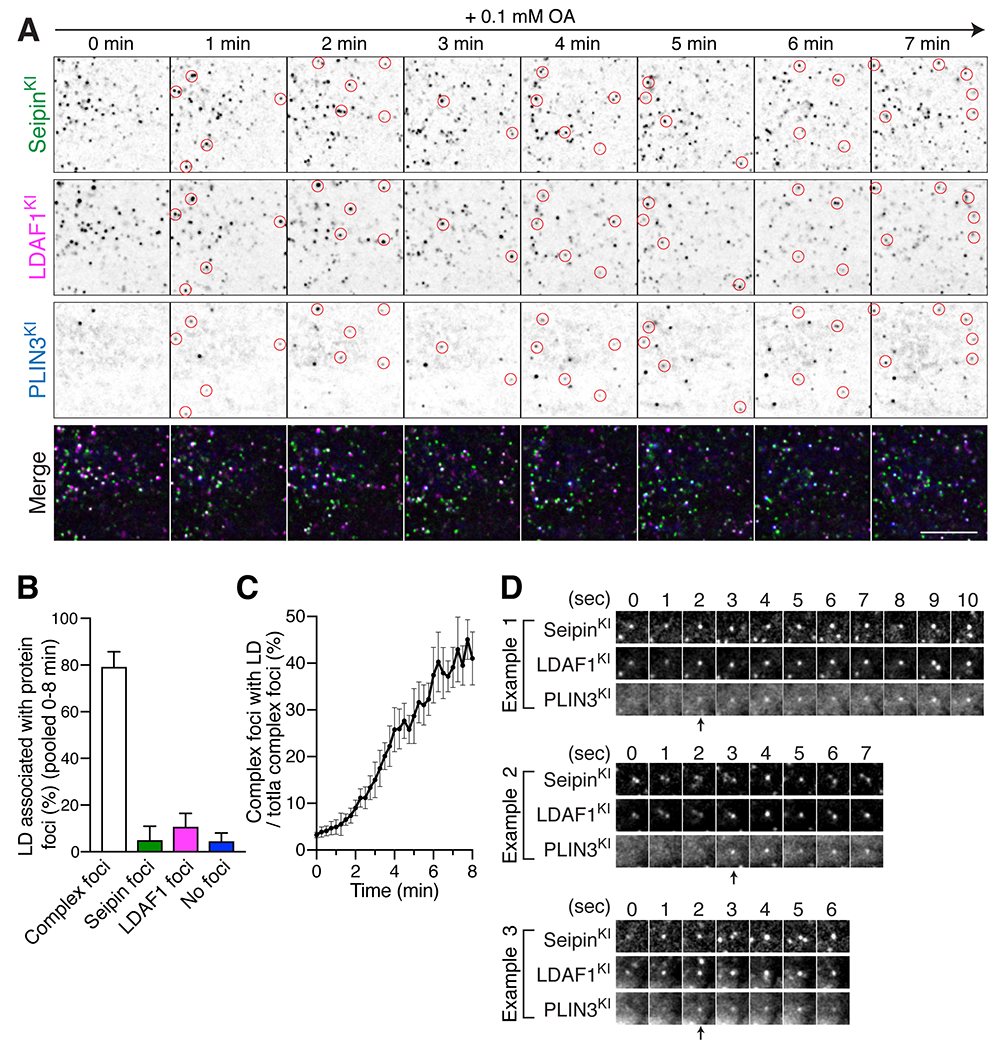
HILO imaging of live SUM159 cells with fluorescent proteins tagged at the seipin locus (sfGFP), LDAF1 locus (mScarlet-i), and PLIN3 locus (HaloTag). Cells were treated with 0.1 mM oleic acid for 3 mins prior to image acquisition shown in (A to D). (A) A representative image shows the localization pattern of endogenous seipin, LDAF1, and PLIN3 every minute after oleate incubation. Red circles indicate newly formed PLIN3-positive LDs and their corresponding positions of seipin and LDAF1 in each frame. Scale bar; 10 μm. (B) A bar graph showing relative fractions of LDs that co-localize with protein foci of seipin and/or LDAF1, as assessed with a TIRF microscope with HILO illumination during LD formation. The LD populations were analyzed at 15-sec intervals for 8 mins. Each timepoint was analyzed and pooled together. Shown are 40 timepoints of individual time-lapse, n = 4 cells, mean ± SD. (C) A graph showing the relative fraction of protein foci composed of seipin and LDAF1 that co-localized with PLIN3 (LD marker) in same time-lapses analyzed in (B). n = 4 cells, mean ± SD. (D) A representative gallery of images showing LD formation at foci where seipin and LDAF1 co-localized.
