Figure 3. Recruitment of LDAF1 to the ER-PM contacts results in LD formation at LDAF1-seipin complex sites.
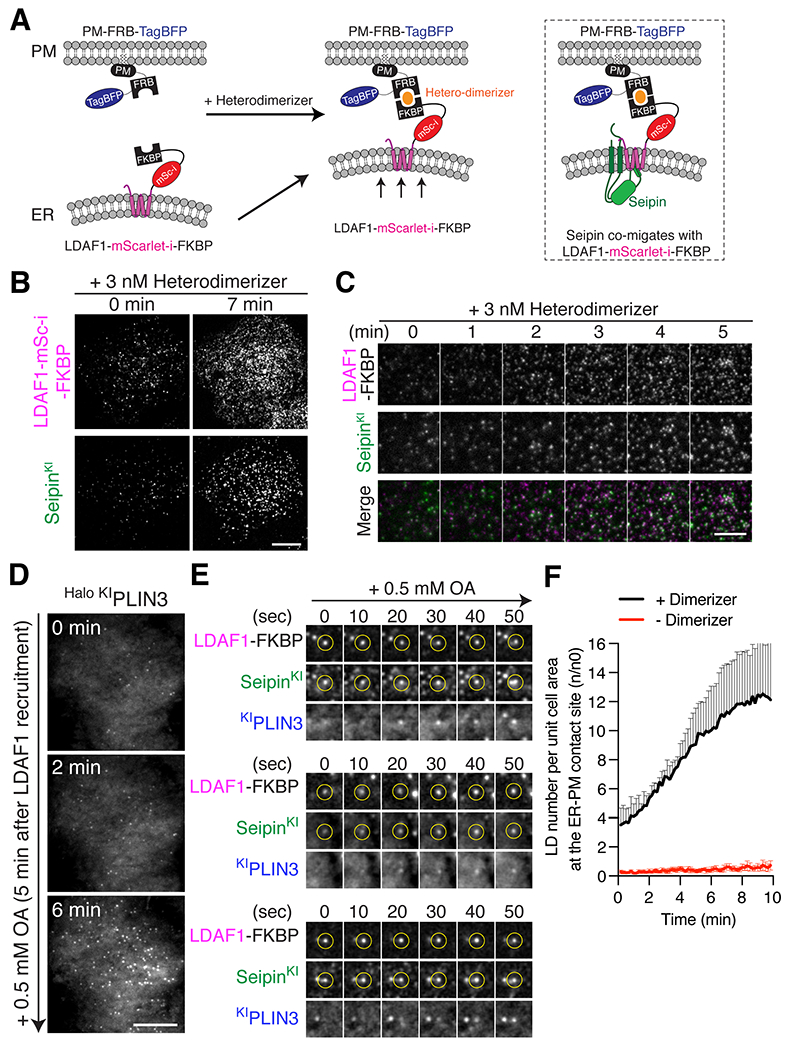
(A) Cartoon depicting the constructs used for the heterodimerizer-dependent acute LDAF1 recruitment assay. Rapalog triggers dimerization of LDAF1-mScarlet-i-FKBP with PM-FRB-TagBFP and thus induces formation of ER-PM tethers. Right panel depicts co-migration of seipin to ER-PM contacts as a complex with LDAF1-mScarlet-i-FKBP. (B and C) TIRF live microscopy showing that recruitment of LDAF1-mScarlet-i-FKBP to the PM with 3 nM heterodimerizer induces co-migration of endogenous seipin to ER-PM contacts. Scale bars, 10 μm (B) and 5 μm (C). (D to F) TIRF live microscopy showing formation of PLIN3-positive LDs at ER-PM contacts after LDAF1 recruitment to the PM. The cells were co-transfected with LDAF1-mScarlet-i-FKBP and PM-FRB-TagBFP and pre-incubated with 3 nM heterodimerizer for 10 mins to induce LDAF1 recruitment to the PM. To induce LD formation, the cells were incubated with 0.5 mM oleic acid. Representative image showing LD formation at ER-PM contact sites (D). Representative time-lapse galleries show formation of LDs at the pre-existing LDAF1-seipin-positive foci (E). Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) Quantification of PLIN3-postiive LD numbers in the TIRF fields after addition of 0.5 mM OA. Cells were either pre-incubated with heterodimerizer (black line) or without heterodimerizer (red line). Mean ± SEM.
