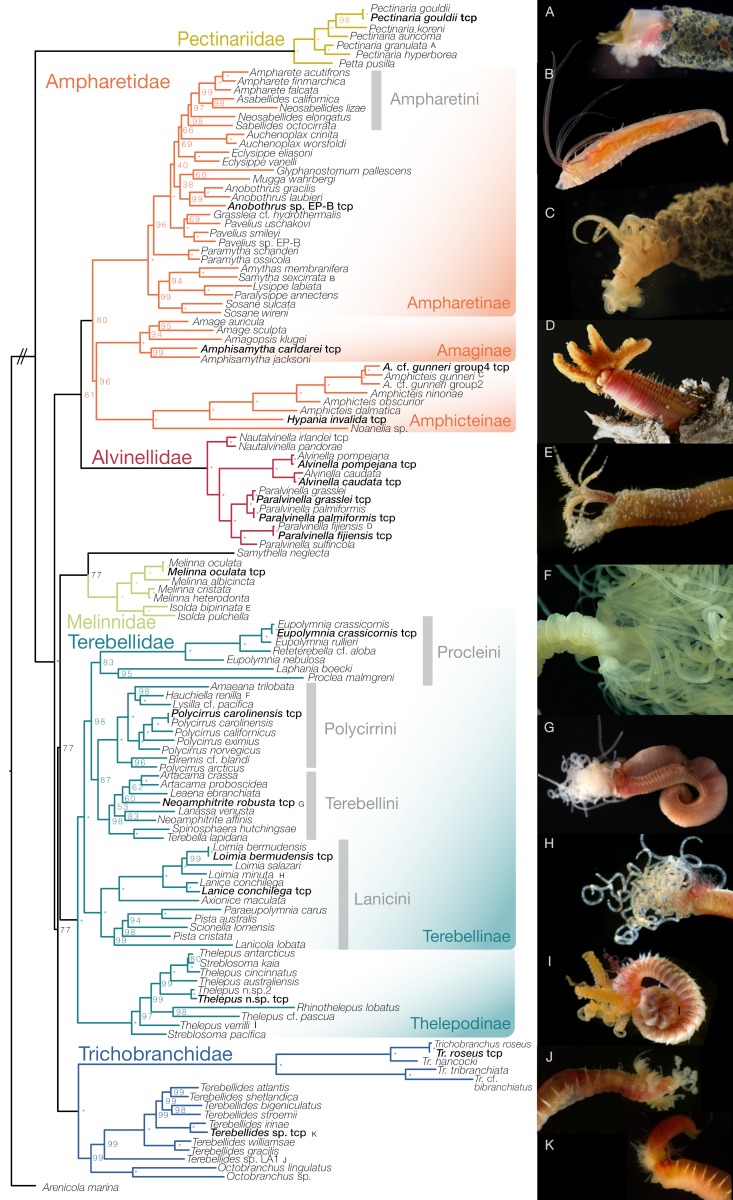
Figure 2.
Relationships among Terebelliformia based on the multigene and morphological dataset (4249 characters) using maximum likelihood and constrained to the transcriptome backbone. Note that bootstrap support was free to vary despite the topological constraint. Asterisks indicate maximum bootstrap support. Terminals in bold are shared with the transcriptome phylogeny. The animals shown on the right are labeled in the phylogeny with letters (A–K). (A) Pectinaria granulata SIO-BIC A9441; (B) Samytha sexcirrata SIO-BIC A1110; (C) Amphicteis cf. gunneri group2 SIO-BIC A1107; (D) Paralvinella fijiensis SIO-BIC A8627 (not the sequenced specimen); (E) Isolda bipinnata SIO-BIC A9437; (F) Hauchiella renilla SIO-BIC A1116; (G) Neoamphitrite robusta SIO-BIC A9453; (H) Loimia minuta SIO-BIC A9452; (I) Thelepus verrilli SIO-BIC A9462; (J) Terebellides sp. LA1 SIO-BIC A9464; (K) Terebellides sp. SIO-BIC A9465.