Fig. 4.
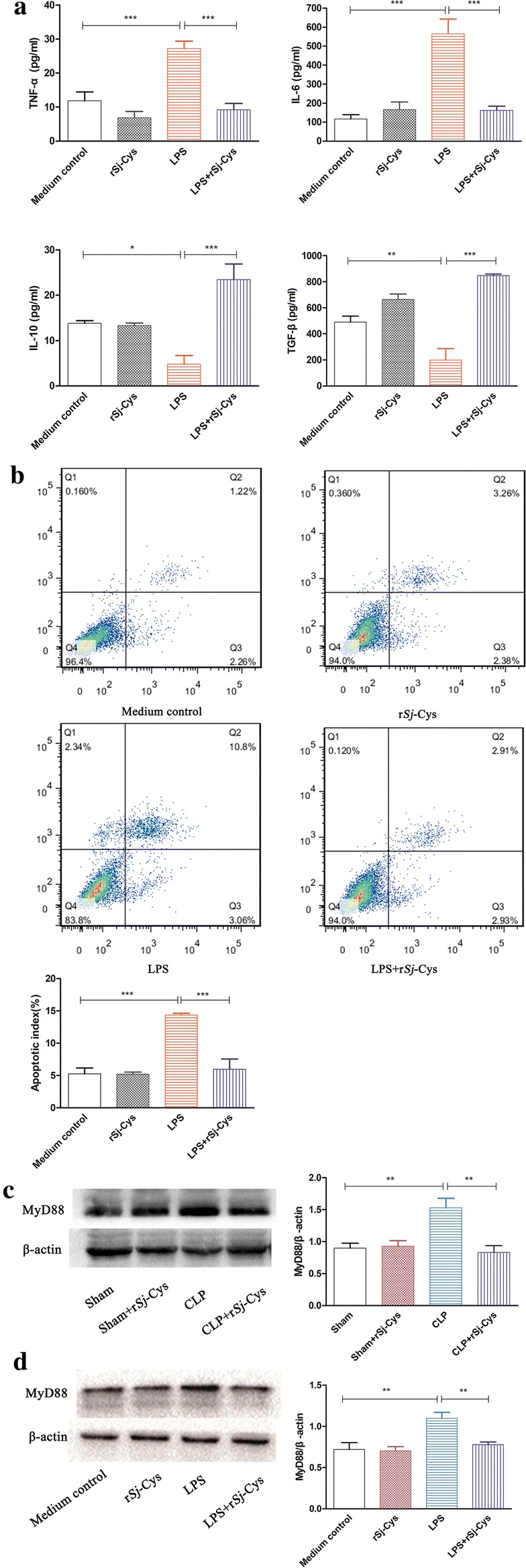
a Incubation with rSj-Cys inhibited the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 and stimulated regulatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β released by LPS-induced H9C2 cells. The levels of these cytokines in the supernatant were measured by ELISA 24 h after incubation. The results are shown as the mean ± SE for each group (n = 3 per group). b rSj-Cys reduced LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis measured by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry images showed the reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rSj-Cys + LPS co-incubated H9C2 cells. The normal H9C2 cells in blank medium or medium with rSj-Cys were used as controls. Data are expressed as mean ± SE from three independent experiments) (n = 3 per group). rSj-Cys treatment suppressed the expression of MyD88 in the myocardial tissues of mice with CLP-induced sepsis (c) (n = 6 mice per group) and in LPS-incubated H9C2 cells (d) (n = 3 per group) measured by western blot. β-actin was measured as a control. The density ratio of MyD88/β-actin is shown on the right. The results are shown as the density mean ± SE for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
