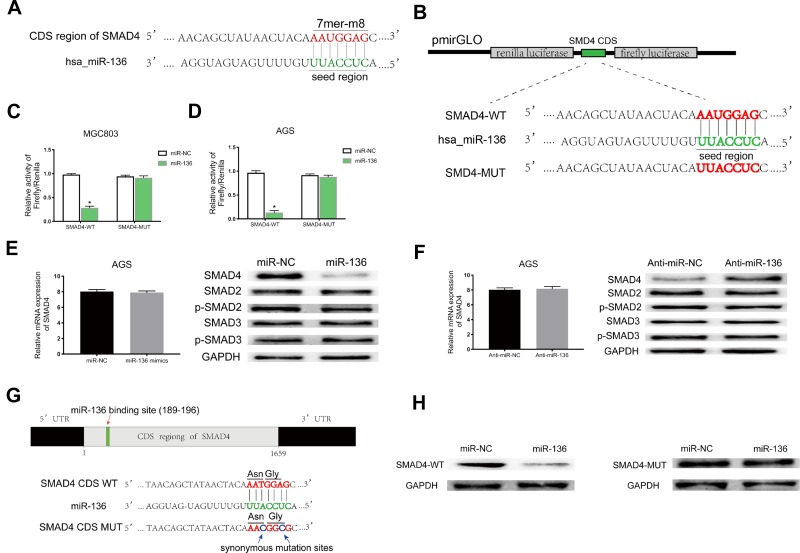
Figure 5.
MiR-136 repressed SMAD4 expression by targeting its CDS. (A) Schematic illustration of the binding site between miR-136 and CDS of SMAD4 predicted by StarBase v3.0 and miRanda. (B) Schematic description about the predicted miR-136-binding locus in SMAD4. Targeting between wild-type/mutant SMAD4 and miR-136 are shown. (C, D) Dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that miR-136 attenuated SMAD4 expression in MGC803 and AGS (*p < 0.05). (E, F) The SMAD4 protein level were decreased/increased significantly when transfected with miR-136 mimics/anti-miR-136 while it’s mRNA level remained nearly unchanged. (G) Schematic illustration of the synonymous mutations at the miR-136-binding location in CDS of SMAD4 (red arrows represent the miR-136-binding location, blue arrows represent the synonymous mutation sites. Asn: AAT replaced by AAC, Gly: GGA replaced by GGG). (H) SMAD4 protein level was dramatically downregulated when cotransfected with pmirGLO-SMAD4-WT and miR-136 mimics compared to the control (pmirGLO-SMAD4-MUT and miR-136 mimics).
Abbreviations: Asn, asparagine; Gly, glycine; CDS, coding sequence; Anti-miR-NC, miR-NC inhibitors; Anti-miR-136, miR-136 inhibitors.