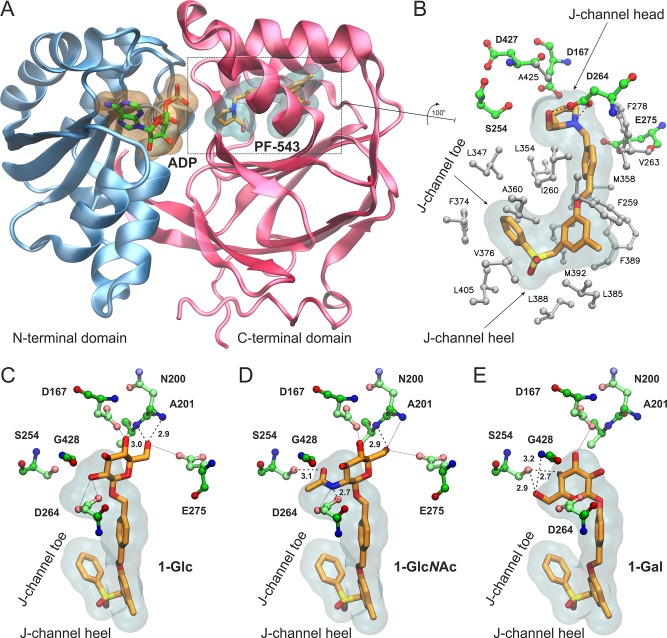
Figure 2.
(A) Structure of SK1 with bound ADP and the inhibitor PF-543 inside the lipid binding channel. SK1 and PF-543 are taken from the crystal structure with PDB ID 4V24(27) and the nucleotide by superimposing with PDB ID 3VZD.28 (B) Close-up view of the Sph-binding site, “J-channel”, illustrating the nonpolar residues (white stick-and-balls) that comprise the foot of the J-channel and the polar residues (green C, blue N, red O) around the polar head of the J-channel. PF-543 is shown with orange C sticks, and dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonding interactions with Asp264 (SK1 isoform 2 numbering as in PDB 4V24). Isoform-specific residue changes at the “toe” and “heel” of the J-channel have been proposed to influence inhibitor selectivity for SK1 versus SK2. (C–E) Bound models of the designed analogues 1-Glc (C), 1-GlcNAc (D), and 1-Gal (E) inside the J-channel of SK1. The translucent surfaces indicate the space occupied by PF-543, whereas polar residues at the head of the J-channel are shown with ball-and-sticks. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines with the heavy-atom distance in Å, whereas putative interactions within 3.5 Å are shown with dotted lines.