Figure 3.
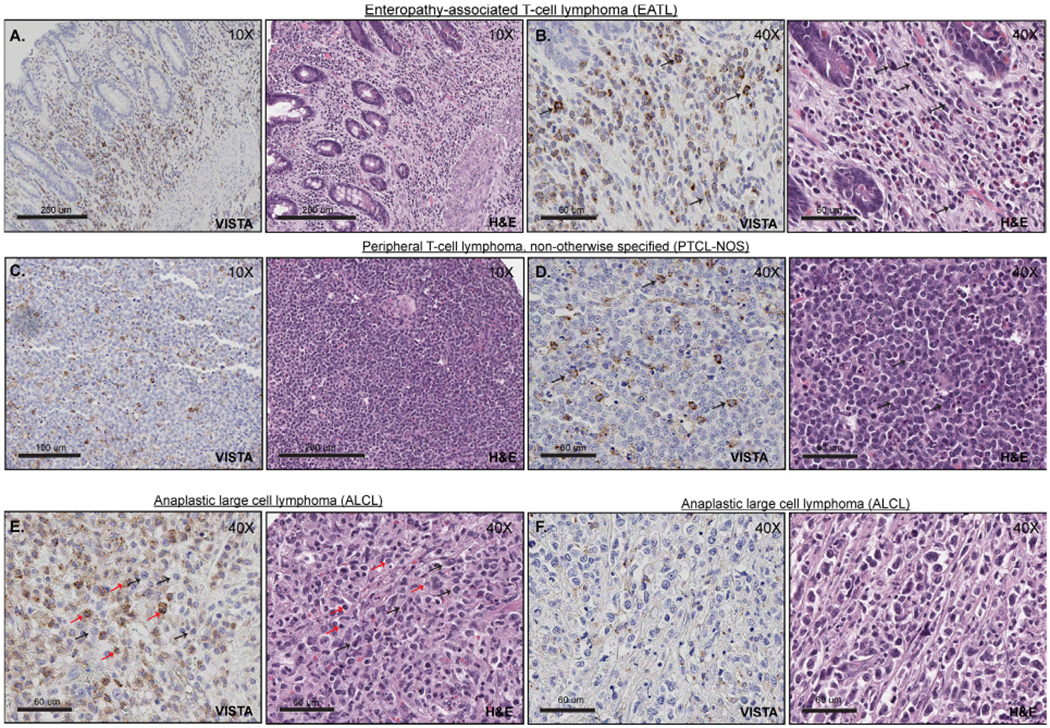
VISTA expression in PTCL. (A and B) Positive expression of VISTA within T cell lymphoma tumour cells (EATL), at low (A) and high magnification (B, 40×). The tumour cells are medium to large in size, with variable amount of cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contours and condensed chromatin (black arrows). (C and D) Positive expression of VISTA within T cell lymphoma tumour cells (PTCL-NOS), at low (C) and high magnification (D, 40×). Tumour cells (black arrows) are small to medium in size with scant cytoplasm, clumped chromatin, irregular nuclear contours and prominent nucleoli. (E) VISTA expression within lymphoma-associated histiocytes and lymphocytes (ALCL). Lymphoma cells are medium to large in size with scant cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin and prominent nucleoli (black arrows). In contrast, reactive lymphocytes are small with plump nuclei (red arrows). (F) Representative image of T cell lymphoma (ALCL) with negative expression of VISTA. ALCL, anaplastic large cell lymphoma; PTCL, peripheral T cell lymphoma; VISTA, V-domain Ig-containing suppressor of T cell activation.
