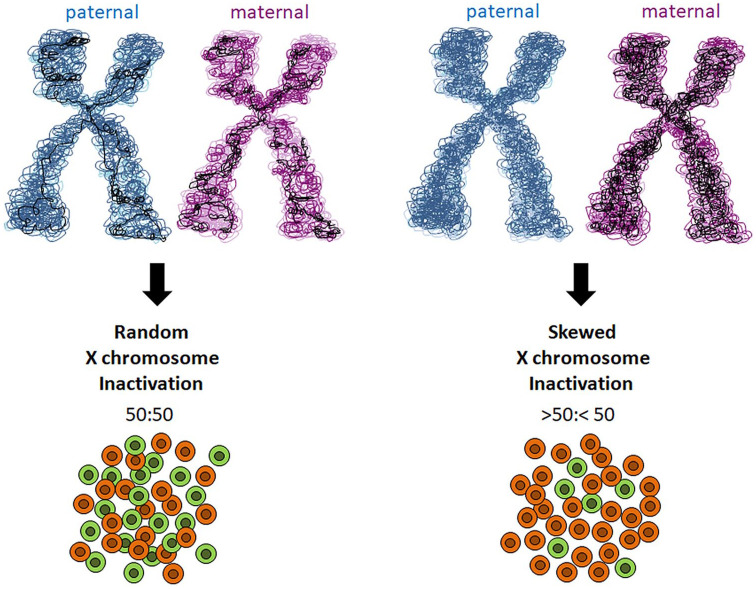
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of skewed X chromosome inactivation. X chromosome inactivation occurs randomly, with an equal probability for the maternally or paternally derived X chromosome to be inactivated, resulting in a mosaic distribution of cells (50:50). Skewed X chromosome inactivation occurs when the inactivation of one X chromosome is favored over the other, leading to an uneven number of cells with each chromosome inactivated (>50:<50).