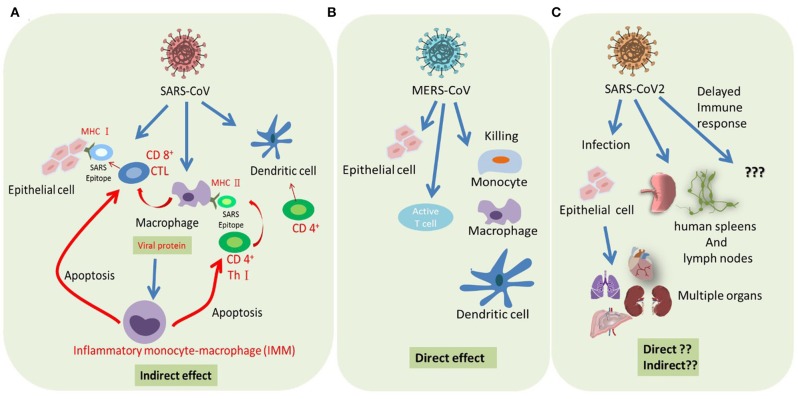
Figure 2.
Summary of host immune response modulated by severe coronaviruses. (A) SARS-CoV infected epithelial cells represents SARS epitope by MHC I to recruit CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL). Macrophage and dendritic cells (DCs) are infected by SARS-CoV and represent SARS epitope by MHC II to recruit CD4+ helper T cells (Th1). Abortive replication of SARS in macrophage impaired its cytokine production, resulting in a delayed IFN response, infiltration of inflammatory monocyte-macrophages (IMMs), and T cells apoptosis. In addition, SARS-CoV infection impaired dendritic cell (DC) function, resulting in reduced T cell activation. (B) Successful replication of MERS-CoV in both alveolar epithelial cells and immune cells resulted in the direct killing of these infected cells. (C) SARS-CoV-2 can probably infect both lung epithelial cells and immune cells and damage the tissue through a direct or cytokine-mediated indirect effect.