FIGURE 11.
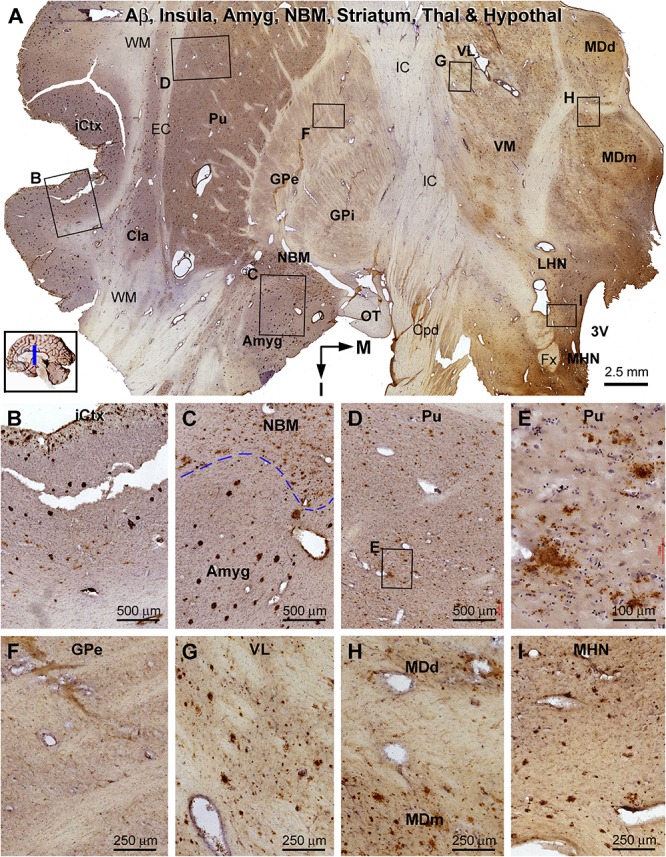
Distribution of β-amyloid deposition in the cerebral, striatal, and diencephalic subregions in an AD brain exhibited Thal phase 5 and Braak V stage neuropathologies. Section orientation, anatomical regions, figure panel arrangement, and scale bars are as indicated. (A) The low-magnification view of Aβ immunolabeling (with toluidine blue counterstain) over the entire section, with individual framed areas enlarged as (B–I). β-Amyloid deposition in the insular cortex and claustrum (Cla) appears as both compact and diffuse-like plaques (A,B). In the amygdala, Aβ plaques appear to be predominantly the compact type, whereas those in the neighboring NBM are manifested as the diffuse-type deposition (C). In the striatum, large amounts of diffuse type Aβ plaques are present in the putamen (Pu) (D,E), whereas little Aβ deposition exists in the globus pallidus (GP) (A,F). Diffuse-like Aβ deposition exists in all thalamic and hypothalamic subdivisions, as shown in enlarged views of the ventrolateral thalamic nucleus (A,G), mediodorsal thalamic nucleus (A,H), and lateral and medial hypothalamic nuclei (A,I). Abbreviations are as defined in Figure 10.
