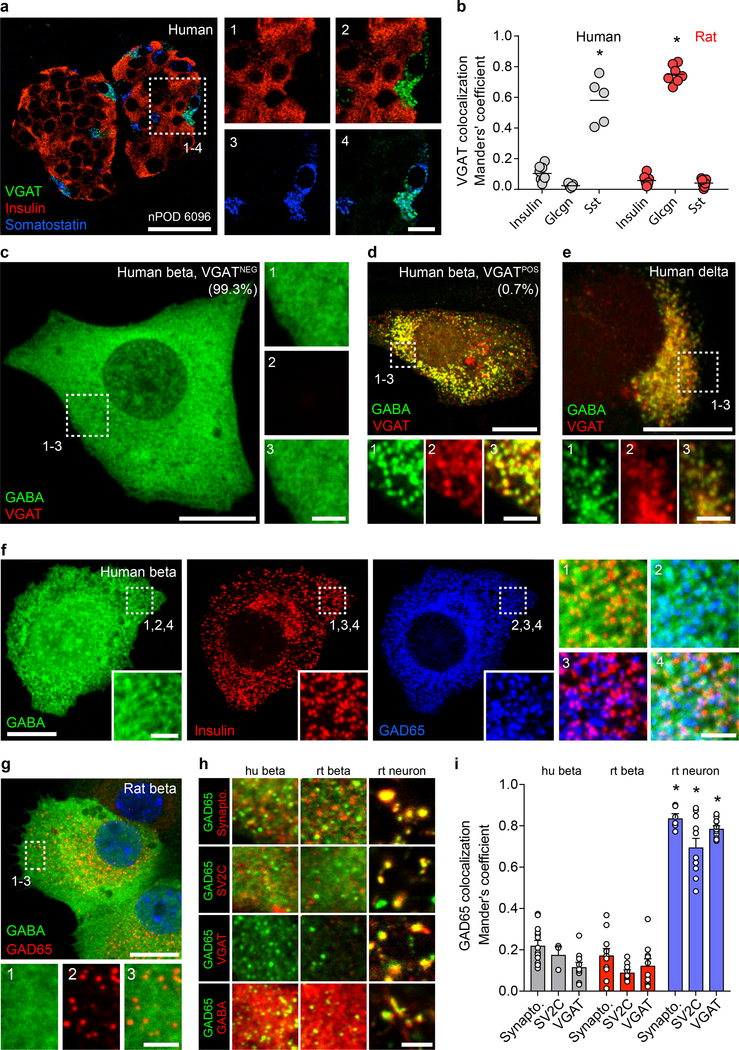
Figure 2. Subcellular localization suggests a non-vesicular GABA release mechanism in beta cells.
a. A human islet from a non-diabetic donor immunostained for VGAT, insulin, and somatostatin. Image is representative of the dataset plotted in panel b. Scale bar 50 μm. Right panels show higher magnification views. Scale bar 10 μm.
b. Expression of VGAT is strongest in human delta cells and rat alpha cells but rare in beta cells of either species. Human islets stained for VGAT and insulin (n =8 islets, 3 donors), glucagon (n = 7 islets, 3 donors), and somatostatin (n = 5 islets, 3 donors). Rat islets stained for VGAT and insulin (n =7 islets, 3 donors), glucagon (n = 6 islets, 3 donors), and somatostatin (n = 6 islets, 3 donors). One-way ANOVA, insulin vs. somatostatin, human (*P < 0.0001), insulin vs. glucagon, rat (*P < 0.0001). Center line indicates the mean.
c. GABA is non-vesicular and cytosolic in almost all human beta cells. A VGATNEG primary human beta cell immunostained for GABA, VGAT, and insulin (not shown). Image is representative of n = 3 human islet preparations, ≥ 3 samples per preparation. Scale bar 50 μm. Right panels show higher magnification views. Scale bar 2 μm.
d. A rare VGATPOS primary human beta cell showing colocalization of GABA and VGAT in vesicular structures. Image is representative of n = 3 human islet preparations, ≥ 3 samples per preparation. Scale bar 50 μm. Bottom panels show higher magnification views. Scale bar 2 μm.
e. A primary human delta cell immunostained for GABA, VGAT, and somatostatin (not shown) showing colocalization of GABA and VGAT in vesicular structures. Image is representative of n = 3 human islet preparations, ≥ 3 samples per preparation. Scale bar 50 μm. Bottom panels show higher magnification views. Scale bar 2 μm.
f-g. GABA is present in the cytosol and does not colocalize with insulin or GAD65 in vesicular structures in primary human (f) or rat (g) beta cells immunostained for GABA, insulin, and GAD65. Images are representative of n = 3 islet preparations, ≥ 3 samples per preparation. Scale bar 10 μm. Inset images show single-channel higher magnification views. Scale bar 2 μm.
h. Colocalization analyses between GAD65 (green) and the synaptic vesicle markers synaptophysin, SV2C, and VGAT (red) or GABA (red) in primary human beta cells, primary rat beta cells, and primary rat hippocampal neurons. Images are representative of data plotted in 2i. Scale bar 2 μm.
i. Quantification of colocalization in human beta cells for GAD65 with markers of synaptic vesicles synaptophysin (n = 14), SV2C (n = 3), and VGAT (n = 10); in primary rat beta cells (n = 11, 10, and 10); and primary rat hippocampal neurons (n = 6, 11, and 11). While GAD65 positive vesicles in rat neurons colocalize with synaptic vesicle markers, colocalization is rare or absent in human and rat beta cells. human beta cells:. Two-way ANOVA: human beta cells vs rat neurons for all markers (*P < 0.0001), rat beta cells vs. rat neurons for all markers (*P < 0.0001).