Figure 2.
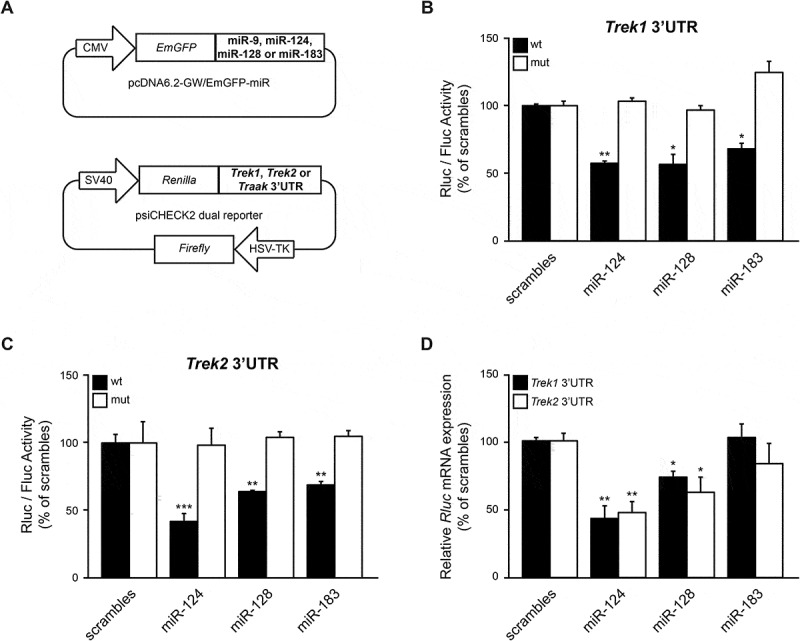
miR-124, miR-128, and miR-183 directly reduce TREK1 and TREK2 reporter protein expression. (A). Schematics of miRNA and TREK reporter constructs. (B, C). HEK293 cells were co-transfected with the TREK1 or TREK2 reporter and pri-miRNA expression vectors and luciferase activity was measured 48 hours later. These assays demonstrated that miR-124, miR-128, and miR-183 significantly reduced TREK1 and TREK2 reporter protein levels, compared to scramble controls. Subsequently, mutagenesis of the predicted miR-124, miR-128, and miR-183 binding sites reversed the inhibitory effect, indicating that these miRNAs directly suppress Trek1 and Trek2 mRNA expression by targeting the specified seed regions in the corresponding 3ʹUTR. (D). HEK293 cells were co-transfected with the Trek1 or Trek2 reporter genes and pri-miRNA expression vectors and Renilla mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR, 48 hours later. Firefly mRNA was used as an internal reference control. This analysis revealed that miR-124 and miR-128 overexpression significantly reduce Trek1 and Trek2 reporter mRNA levels, compared to scramble controls, indicating that these miRNAs drive Trek1 and Trek2 mRNA degradation. Data show the mean ± SEM from 6 independent transfections (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
