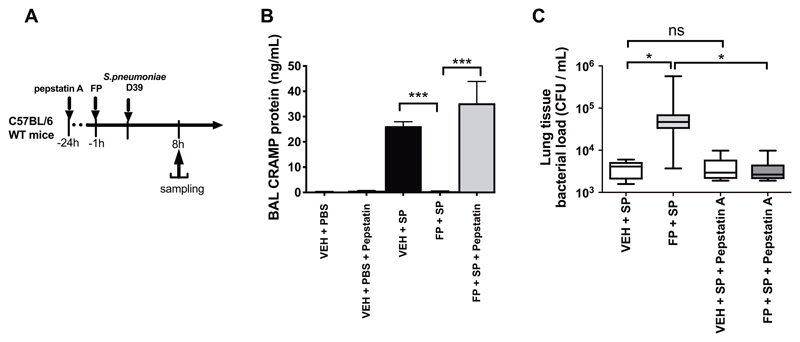
Figure 6. Inhibition of cathepsin D reverses FP-mediated suppression of cathelicidin and restores lung bacterial control.
(A) Experimental outline. C57BL/6 mice were treated with 60mg/kg intraperitoneal pepstatin-A, 24 hours prior to intranasal treatment with 20μg fluticasone propionate or vehicle control and challenge with S. pneumoniae D39. (B) CRAMP concentrations in BAL were measured by ELISA at 8h post-infection. (C) Lung bacterial loads were measured by quantitative culture at 8 hours post-infection. Data in (B) shown as mean (+/- S.E.M). Bacterial load data in (C) displayed as box and whisker plots showing median (line within box), IQR (box) and minimum to maximum (whiskers). Animal experiments comprise n=8-10 mice/group, representative of at least two independent experiments. Data analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. n.s. non-significant *p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.001.