Figure 2. TSGL-Ig attenuates pulmonary vaso-occlusion in SCD mice.
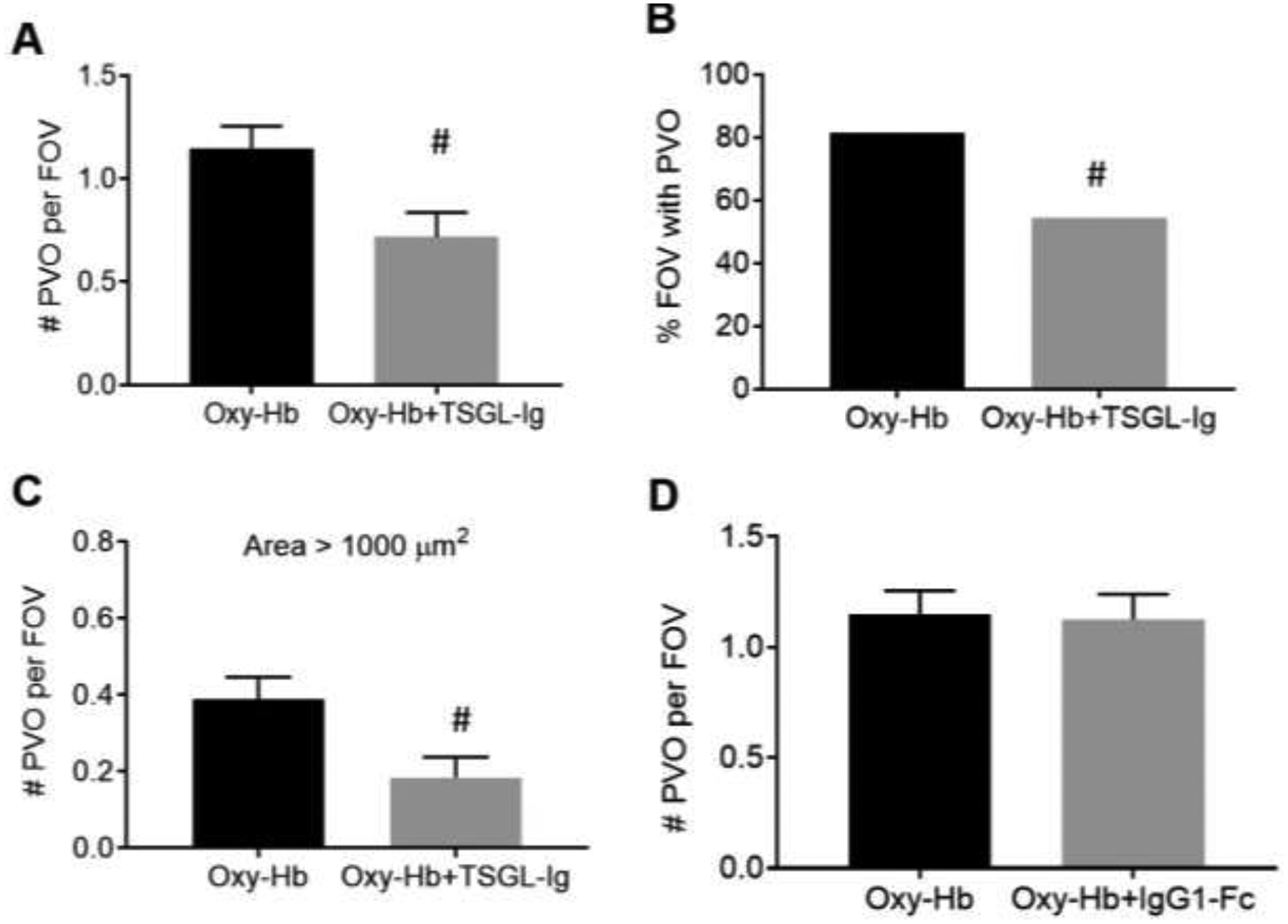
Time series of qFILM images were analyzed in 10–12 field of views (FOV~65,536 μm2) per mouse and 3 to 4 mice per treatment group to determine average number of pulmonary vaso-occlusions per FOV, percent FOVs with pulmonary vaso-occlusions, and average number of large pulmonary vaso-occlusions (area > 1000 μm2) per FOV. Means were compared using unpaired Student’s t test and percents were compared using four-fold table analysis with χ2 statistics to assess the effect of TSGL-Ig or rh IgG1-Fc on IV oxy-Hb triggered lung vaso-occlusion in SCD mice. Treatment with TSGL-Ig significantly reduced (A) average number of pulmonary vaso-occlusions per FOV, (B) percent FOVs with pulmonary vaso-occlusions, and (C) average number of large pulmonary vaso-occlusions per FOV in SCD mice. (D) Average number of pulmonary vaso-occlusions per FOV was not affected by IV administration of control rh IgG1 Fc. Error bars SE. # p < 0.05. IV Oxy-Hb SCD (n = 4 mice); IV Oxy-Hb + TSGL-Ig SCD (n = 3 mice); IV Oxy-Hb + rh IgG1-Fc SCD (n = 3 mice). PVO, pulmonary vaso-occlusion,
