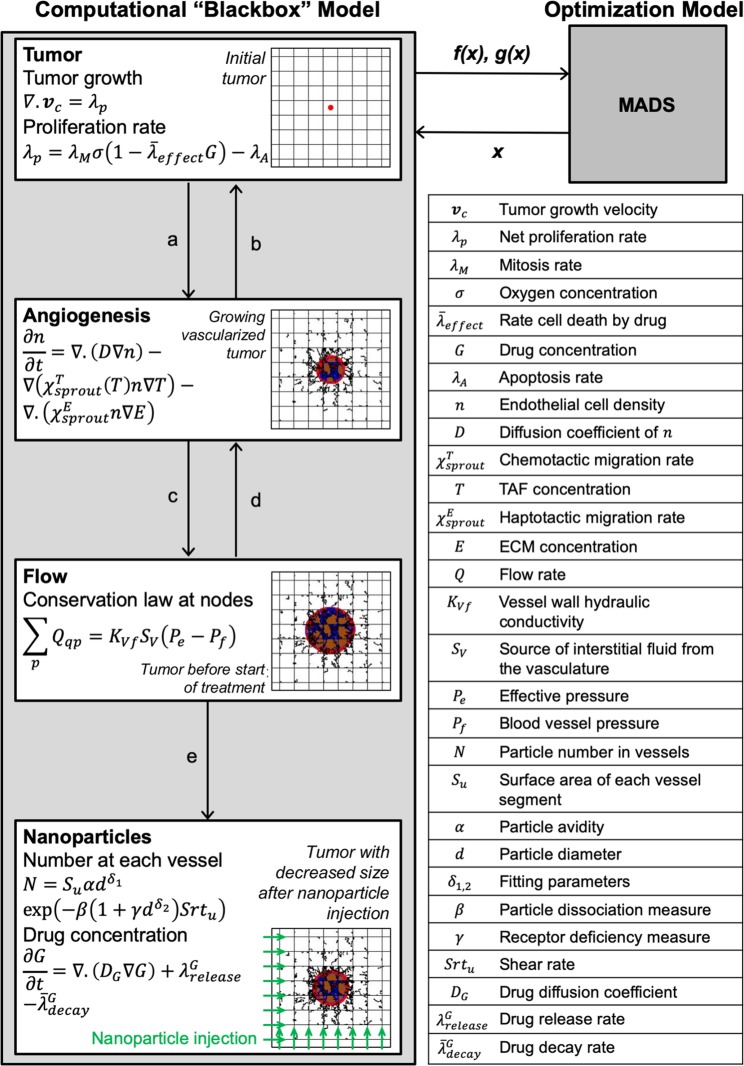
Figure 4.
Hybrid framework for optimizing nanoparticle mediated drug delivery. The framework couples a computational “blackbox” model of vascularized tumor growth and nanoparticle treatment7,25 with an optimization model based on the mesh adaptive direct search (MADS) algorithm26,27. The computational model25 uses a nanoparticle design (x) selected by MADS and evaluates the objective function f(x) and the constraints g(x). These values are used by MADS to recommend a new trial point for the computational model. This process iterates until the objective function is optimized, so that the result of the hybrid framework generates optimal nanoparticle designs x*. In the computational model, multiple sub-models interact and exchange parameters, including: (a) angiogenic factors; (b) oxygen and nutrients; (c) location of capillary junctions; (d) wall shear stress, flow stimulus, and intravascular pressure; and (e) vessel radii, vessel surface areas, and flow rate. The tumor is displayed in the computational model at inception, after vascularization, before treatment and after treatment. Colors are as in Fig. 1.