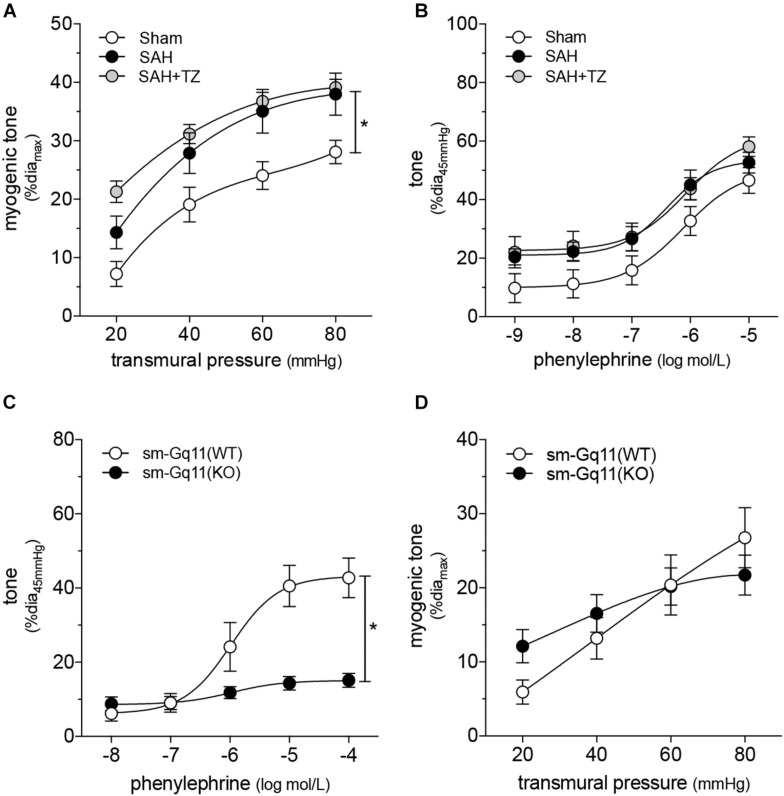
FIGURE 7.
Cerebral and cremaster resistance arteries have distinct phenotypes. (A) Terazosin (TZ; twice daily for 2 days with i.p. injections; 1 mg/kg initial pre-operative dose followed by 0.5 mg/kg for all subsequent injections) does not normalize the augmented myogenic reactivity observed in olfactory cerebral arteries isolated from mice at 2-days post-SAH induction (sham diamax: 108 ± 4 μm, n = 6; SAH diamax: 104 ± 7 μm, n = 5; SAH + TZ diamax: 101 ± 9 μm, n = 5). (B) Phenylephrine responses in olfactory cerebral arteries are unaffected by SAH or terazosin treatment (sham diamax: 110 ± 4 μm, n = 5; SAH diamax: 104 ± 7 μm, n = 5; SAH + TZ diamax: 108 ± 10 μm, n = 6). (C) Phenylephrine-stimulated vasoconstriction is abolished in olfactory cerebral resistance arteries isolated from smooth muscle cell-targeted Gq11 knockout mice [sm-Gq11(KO); diamax = 156 ± 5 μm, n = 10], relative to wild-type littermate controls [sm-Gq11(WT); diamax = 144 ± 5, n = 5]. However, (D) there is no effect of the targeted Gq11 gene deletion on myogenic tone. *P < 0.05.