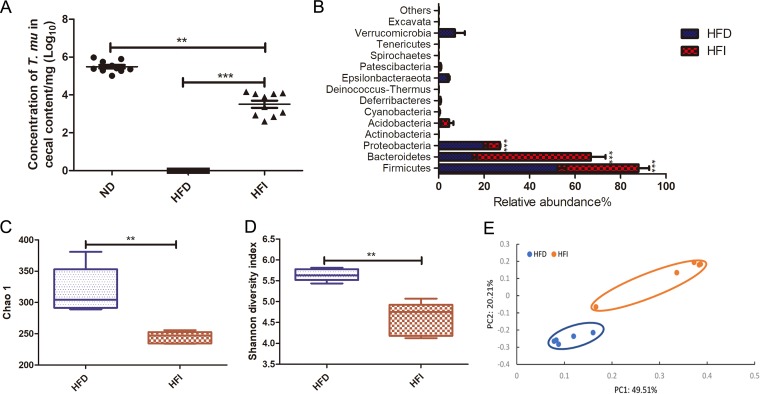
FIG 4.
HFD-induced T. musculis colonization reduction was at least partially due to the limited amount of fermentable dietary fiber in the food. T. musculis-negative WT B6 mice fed ND were orally administered purified T. musculis on day 0, and on the next day, the food was switched to the specific type of diet as indicated. Two weeks later, the cecal contents were collected, and the presence of T. musculis was examined microscopically. (A) The concentration of T. musculis per milligram of cecal contents from the mice fed the indicated types of diet. The experiments were performed 3 times, and there was a total of 9 to 10 mice in each group. (B) The relative abundance of cecal bacterial phyla from the mice fed HFD or HFI. (C) Shannon index showing commensal bacterial community diversity. (D) Chao1 index showing commensal bacterial community richness. (E) PCoA based on OTU abundance of the cecal bacteria. Each symbol represents one individual mouse. In panels B to D, there were 5 mice in each group. The error bars represent standard deviations. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; HFD, high-fat diet; HFI, HFD plus 10% inulin; T. mu, T. musculis.