FIG 6.
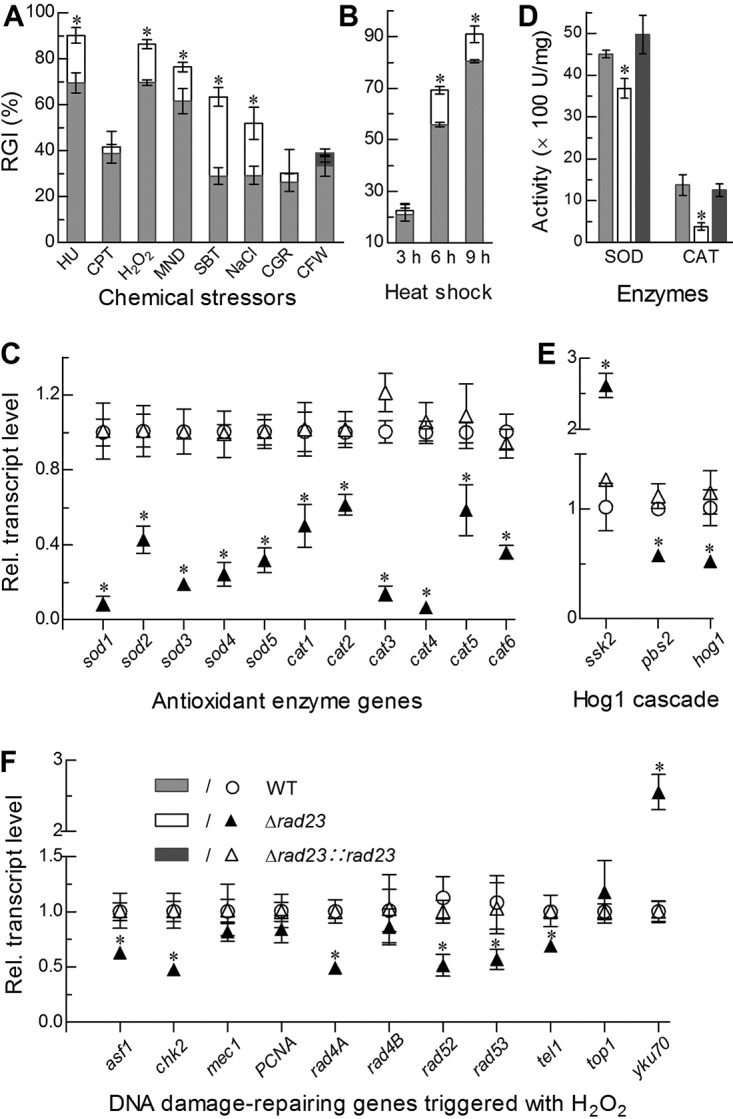
Imapcts of rad23 deletion on cell sensitivities to stress cues and expression levels of stress-responsive enzyme genes. (A, B) Relative growth inhibition (RGI) of fungal colonies by hydroxyurea (HU; 10 mM), camptothecin (CPT; 1 μM camptothecin), H2O2 (2 mM), menadione (MND; 0.02 mM), NaCl (0.4 M), sorbitol (SBT; 1 M), Congo red (CGR; 3 μg · ml−1) or calcofluor white (CFW; 5 μg · ml−1) after an 8-day incubation on CDA at 25°C and by the time of heat shock at 42°C during 8 days of growth on SDAY at 25°C, respectively. (C, D) Relative transcript (RT) levels of all SOD and CAT genes in the 3-day-old SDAY cultures of rad23 mutants versus the WT, and total SOD and CAT activities quantified from the protein extracts of the same cultures. (E) RT levels of hog1 and two upstream genes in the 3-day-old SDAY cultures of rad23 mutants versus the WT. (F) RT levels of DNA damage-repairing genes in the 3-day-old cultures of rad23 mutants versus the WT cocultivated with 2 mM H2O2 on SDAY at 25°C. The asterisk marked on a given phenotype of the Δrad23 mutant denotes a significant difference from the same phenotype of two unmarked control strains (Tukey’s HSD, P < 0.05). Error bars indicate standard deviations from three replicates.
