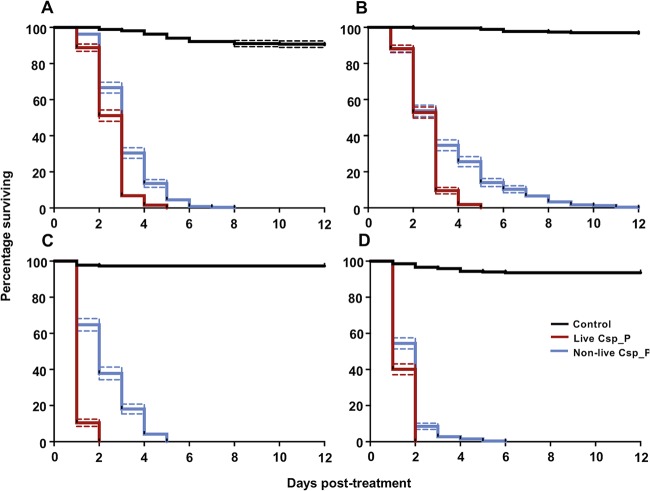
FIG 2.
Nonlive Csp_P effectively kills the larvae of important mosquito vector species, including those resistant to common chemical insecticides. At 3 days posthatching, larvae from the Ae. aegypti ROCK strain (A), the pyrethroid-resistant Ae. aegypti strain NR-48830 (B), the An. gambiae Keele strain (C), and the Cx. quinquefasciatus JHB strain (D) were fed an attractive pellet containing fishmeal and 20% gelatin. Larvae were treated with one of three different types of pellets: no-bacterium controls (black lines), live Chromobacterium Csp_P (red lines), or nonlive Chromobacterium Csp_P (blue lines). Nonlive Csp_P was an effective larvicide for each line, with average times to death ± the standard errors of the mean (SEM) of 3.13 ± 0.08 days for ROCK, 3.40 ± 0.13 days for NR-48830, 2.25 ± 0.09 days for Keele, and 1.68 ± 0.05 days for JHB. Larvae were reared in groups of 25 to 30 in 300 ml of deionized water. Lines depict the percentages of larvae surviving at each day posttreatment (± SEM) for three experimental replicates, with each containing three cages per treatment.