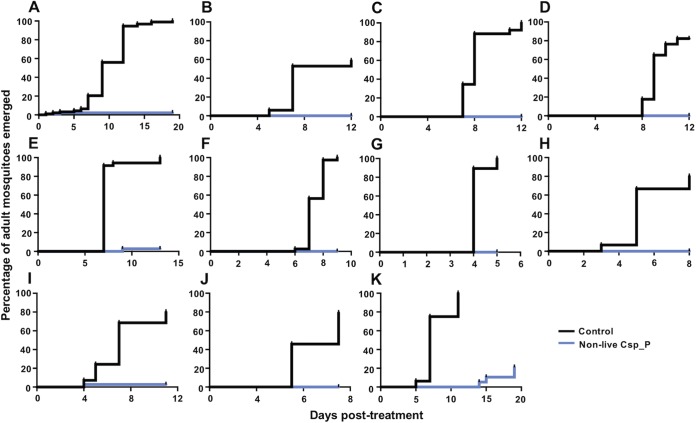
FIG 6.
Nonlive Csp_P powder effectively prevents adult mosquito emergence from translocated breeding sites under semi-field conditions. Mosquito breeding sites were located at various sites around eastern Puerto Rico. The water and any larvae and pupae were removed from the breeding site and moved to the semi-field cage in sterile containers. Larvae and pupae were counted and, along with the water and any detritus, divided evenly between a control treatment (black lines) and a nonlive Csp_P treatment (blue lines). Adult emergence was monitored since it was too difficult to locate dead L1 and L2 larvae in the opaque breeding site water. Across eleven different breeding sites, we observed that 342/374 adults emerged from the control treatment compared to 9/374 from the nonlive Csp_P treatment (Fisher exact test: P < 0.0001). Breeding sites contained either Ae. aegypti larvae (n = 5), Cx. quinquefasciatus larvae (n = 2), or a mix of both (n = 4). Breeding sites were collected from the following receptacles: tire (A), paint pail (B), water meter (C), plastic cup (D), bucket (E), container (F), bucket (G), pipe (H), bucket (I), container (J), and wastewater tank (K). Lines depict the percentages of adults that had emerged from the breeding site water at different intervals posttreatment.