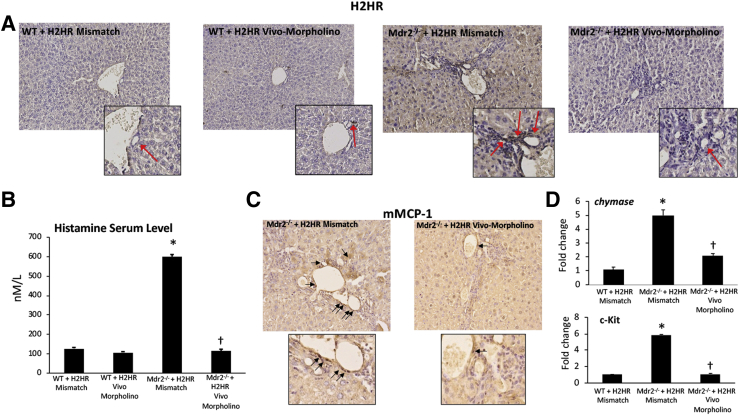
Figure 2.
Evaluation of histamine-2 receptor (H2HR)/histamine signaling and mast cell (MC) presence. A: There is little expression of H2HR in wild-type (WT) groups as shown by immunohistochemistry; however, multidrug-resistance transporter 2/ABC transporter B family member 2 knockout [Mdr2−/− (ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 4 null)] mice treated with mismatch have increased biliary H2HR expression (primarily in large cholangiocytes; red arrows) that is lost in mice treated with H2HR vivo-morpholino. In Mdr2−/− mice treated with mismatch, there is an increase in histamine serum levels (B) and MC presence (C; black arrows); however, Mdr2−/− mice treated with H2HR vivo-morpholino have decreased histamine secretion and fewer MCs. D: MC marker expression, chymase, and c-Kit were determined by quantitative real-time PCR, and there is an increase in Mdr2−/− mice treated with H1HR mismatch compared with WT mice, whereas expression is decreased in Mdr2−/− mice treated with H2HR vivo-morpholino. No differences were found between WT groups (data not shown). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 16 experiments for enzyme immunoassay (EIA); n = 12 experiments for real-time PCR. ∗P < 0.05 versus WT mismatch; †P < 0.05 versus Mdr2−/− mice + H2HR vivo-morpholino. Original magnification: ×40 (A and C, main images); ×100 (A and C, insets). mMCP-1, mouse MC protease-1.