Figure 4.
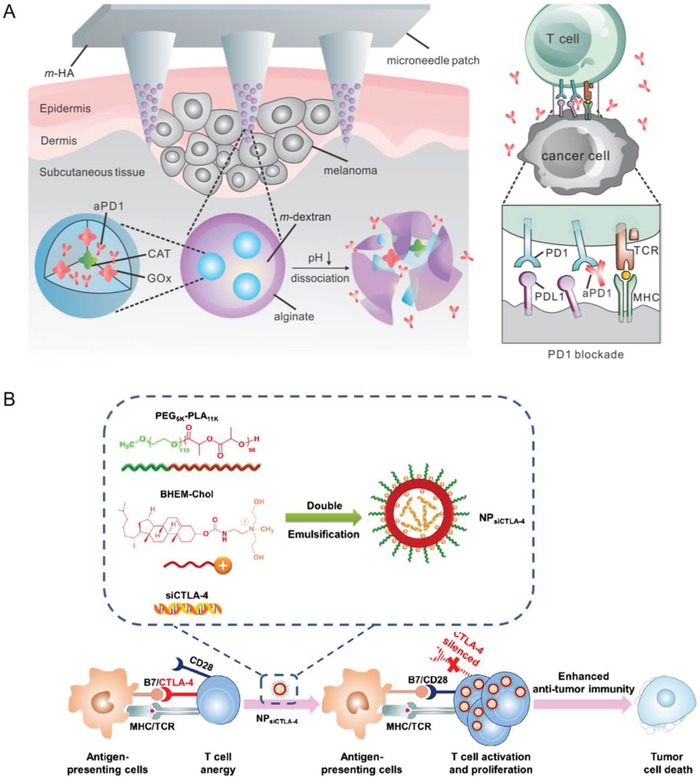
Nanoparticle‐mediated immune checkpoint modulation to enhance anti‐tumor functions of T cells. A) Schematic of the microneedle patch‐assisted delivery of aPD1 for the skin cancer treatment. The aPD1 and GOx/CAT enzymatic system were loaded inside the NPs and delivered by a microneedle patch. The enzyme‐mediated conversion of blood glucose to gluconic acid promotes the sustained dissociation of NPs, subsequently leading to the release of aPD1. The immune system was activated to destroy skin cancer cells through the blockade of PD‐1 by aPD1. Reproduced with permission.[ 100 ] Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society. B) Enhanced T‐cell‐mediated immune responses and anti‐tumor efficacy were achieved by blocking CTLA‐4 using siCTLA‐4‐encapsulated nanoparticles (NP siCTLA‐4). NP siCTLA‐4 was prepared with poly(ethylene glycol)‐block‐poly(d,l‐lactide) and a cationic lipid BHEM‐Chol by double emulsification. Reproduced with permission.[ 102 ] Copyright 2016, Elsevier.
