Figure 12.
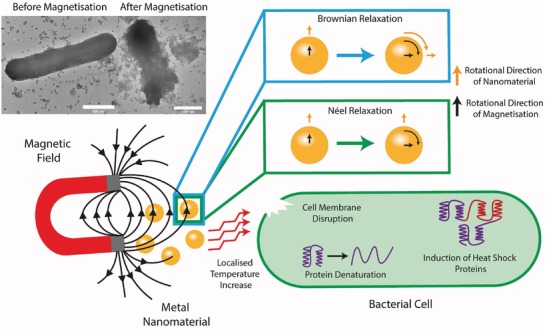
Schematic representation of the mechanism of magnetic hyperthermia of superparamagnetic nanomaterials and subsequent antimicrobial mechanism. The conversion of an external magnetic field to heat occurs due to Brownian relaxation, in which the entire nanomaterial rotates and Néel relaxation, in which only the magnetization rotates, generating localized increases in temperature which is responsible for the antimicrobial activity. Top left, scanning electron micrographs of E. coli before (left) and after (right) magnetic hyperthermia treatment. Reproduced with permission.[ 255 ] Copyright 2017, Wiley‐VCH.
