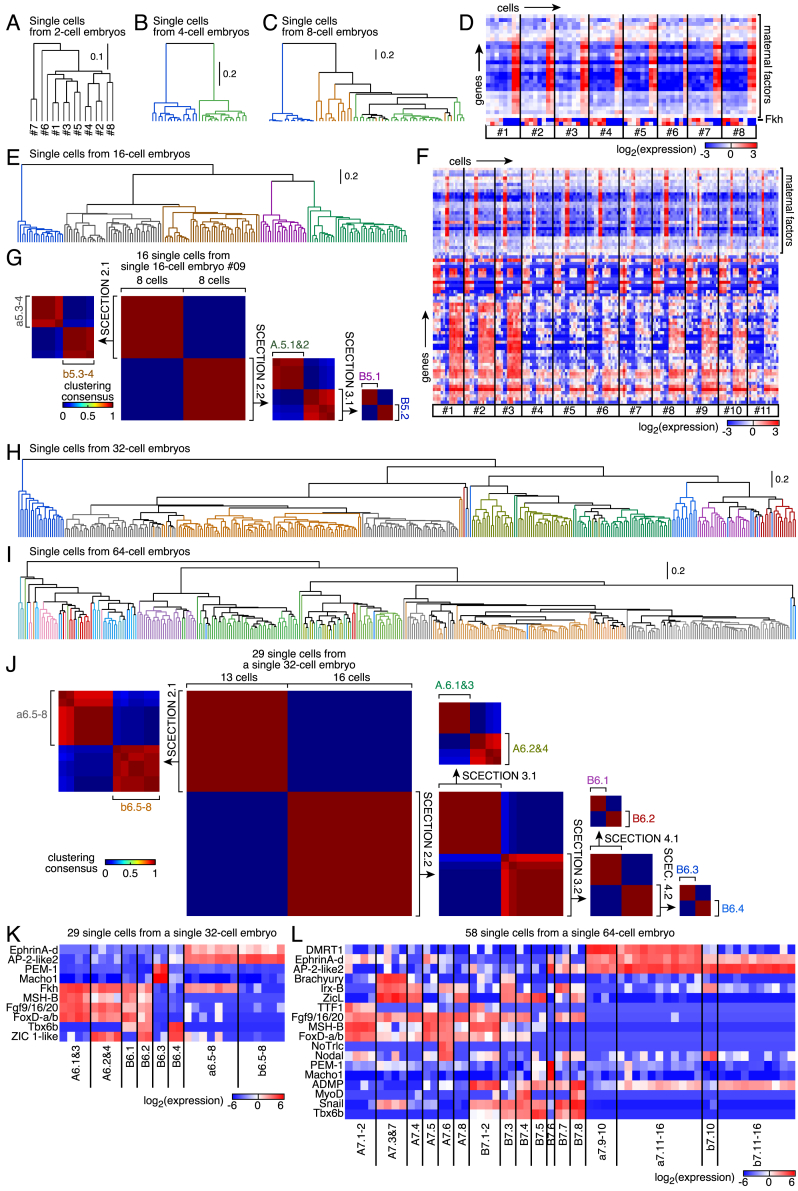
Figure S2.
Classification of Single-Cell Gene Expression Profiles, Related to Figure 2
(A) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 2-cell embryos (embryo numbers are indicated).
(B) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 4-cell embryos (branches are colored according to the cell type).
(C) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 8-cell embryos (branches are colored according to the cell type).
(D) Expression levels (as measured by scRNA-Seq) of genes that classify single cells of 8-cell embryos into three cell types.
(E) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 16-cell embryos (branches are colored according to the cell type).
(F) Expression levels (as measured by scRNA-Seq) of genes that classify five cell types in single cells of 16-cell embryos.
(G) SCECTION identifies five cell types in 16-cell embryos.The groups of two cells that inherit the maternal factors belong to the germ cell lineage and are transcriptionally silent at that stage.
(H) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 32-cell embryos (branches are colored according to the cell type determined by SCECTION).
(I) Hierarchical clustering of single-cell transcriptome profiles of 64-cell embryos (branches are colored according to the cell type determined by SCECTION).
(J) SCECTION applied to 29 single cells from an individual 32-cell embryo. SCECTION identified 8 cell types (SCEC.: SCECTION).
(K) Expression levels (as measured by scRNA-Seq) of genes that classify 8 cell types in 29 single cells of a single 32-cell embryo.
(L) Expression levels (as measured by scRNA-Seq) of genes that classify 17 cell types in 58 single cells of a single 64-cell embryo.