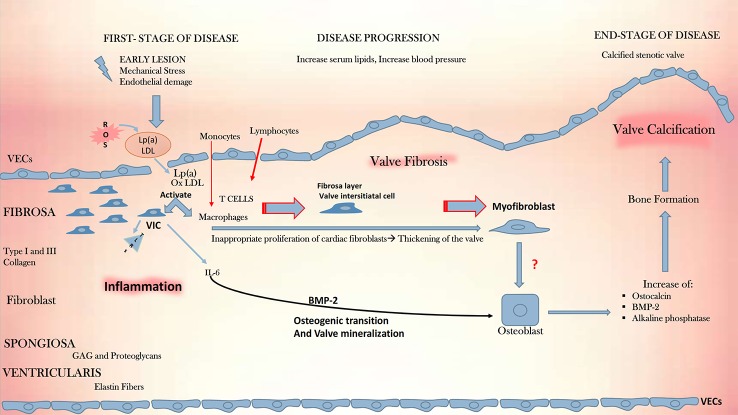
Figure 2.
CAVD development. Depicted is the pathophysiologic cascade leading to CAVD. Initial lesions, such as mechanical stress, endothelial damage and, production of ROS, initiate an ox-LDL-mediated inflammation in the endothelium and promote the activation of macrophages and quiescent VICs. These start to express TLRs and the cytokine pro -inflammatory IL-6, which plays a fundamental role in inflammation, together with macrophages and T cells. IL-6 mediates mineralization through the BMP-2 signal, driving the osteogenic transition and culminating with the aortic valve calcification. CAVD, calcific aortic valve disease; GAG, glycosaminoglycans; IL-6, interleukin 6; Lp(a), lipoprotein a; ox-LDL, oxidized low-density lipoprotein; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLRs, toll-like receptors, VECs, valve endothelial cells; VICs, vascular interstitial cells, BMP-2, bone morphogenetic protein 2.