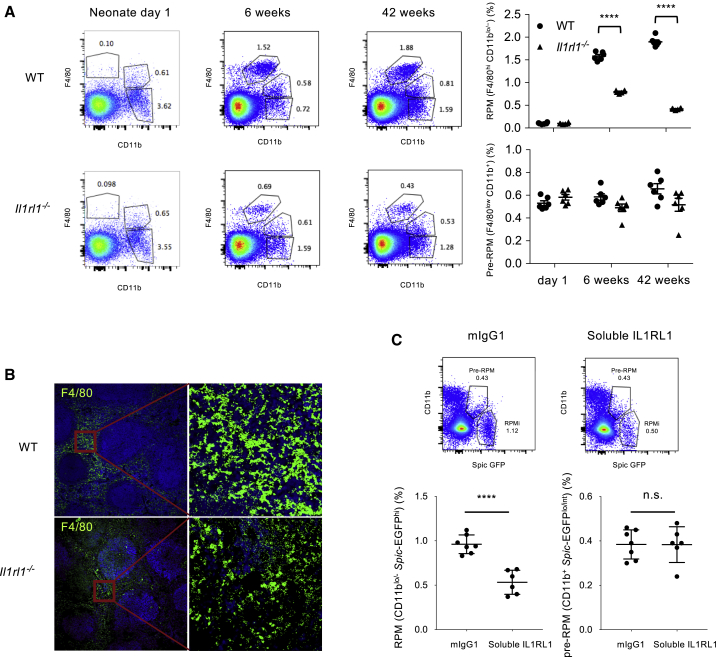
Figure 2.
IL1RL1 Signaling Controls the Development of Splenic Red Pulp Macrophages (RPMs)
(A) Quantification (percentage among CD11clow Ly6Glow NK1.1low SSC-Alow cells) of splenic pre-RPMs (CD11bhi F4/80lo) and RPMs (CD11blo/− F4/80hi) in neonates (Day 1), young (6 weeks), and old (42 weeks) WT and Il1rl1−/− mice. Each dot represents a separate mouse. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(B) Staining of RPMs (F4/80 shown in green) in spleen sections of 42-week WT and Il1rl1−/− mice.
(C) Flow cytometry staining and quantification of splenic RPMs (CD11blo/Spic-EGFPhi) and pre-RPMs (CD11b+Spic-EGFPlo/int) (percentages among CD11clow Ly6Glow NK1.1low SSC-Alow cells) after 6 weeks of treatment of Spicigfp/igfp reporter mice with control murine IgG1 (mIgG1) or soluble IL1RL1-murine Fc fusion protein (soluble IL1RL1). Each dot in the quantification panels represents a separate mouse. Data represent mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001.
Please also see Figures S2 and S3.