Figure 3.
Ded1p Has an Intrinsic Property to Form Condensates upon Elevated Temperature
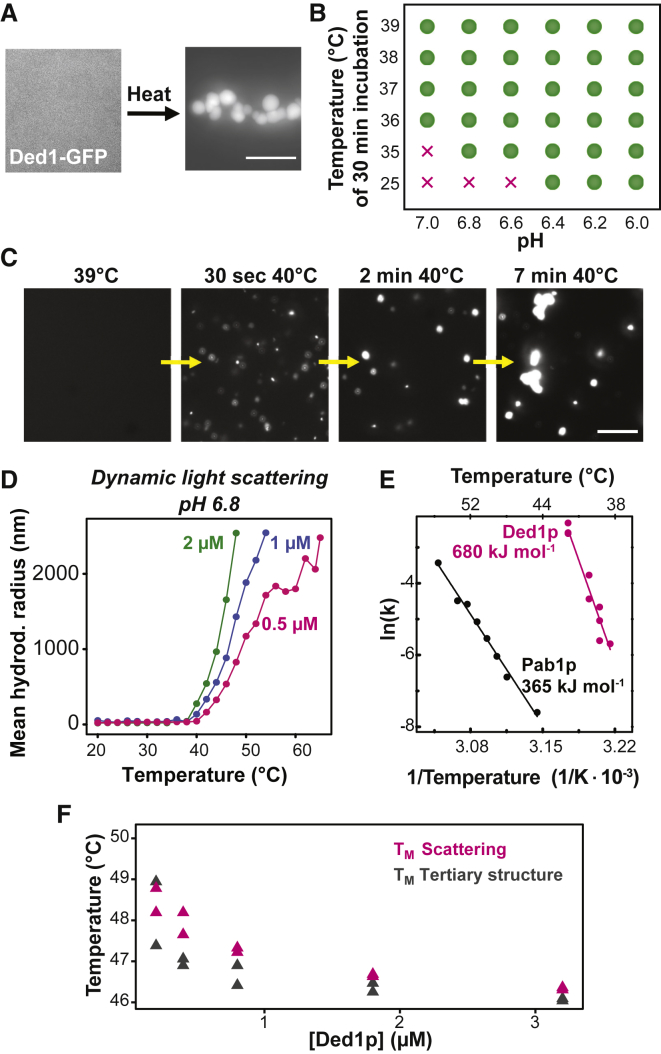
(A) Fluorescence image of 2 μM purified Ded1-GFP in piperazine-N,N′-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid (PIPES)/KOH buffer (pH 7) and 100 mM KCl buffer at 25°C (left image) and after 10 min at 42°C (right image). Scale bar, 3 μm.
(B) Phase diagram of Ded1p in PIPES/KOH and 100 mM KCl buffer with the control parameters pH and temperature. Analysis was performed after 30 min of incubation. Green dots indicate condensates, and “x” indicates no condensates.
(C) Images from a time-lapse video monitoring Ded1p assembly at pH 6.8. Scale bar, 15 μm.
(D) Hydrodynamic radius of 0.5, 1, and 2 μM Ded1-GFP in PIPES/KOH (pH 6.8) and 100 mM KCl buffer as a function of temperature.
(E) Kinetic analysis of the apparent Ded1-GFP and Pab1-GFP assembly reaction, measured by DLS in PIPES/KOH (pH 6.8) and 100 mM KCl buffer. Plotted is the natural logarithm of the apparent rate constant (ln(k)) as a function of the reciprocal temperature.
(F) Analysis of the transition temperature midpoints of Ded1p condensation as determined by light scattering (TM scattering) and changes in tertiary structure as determined by nano-differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF) (TM tertiary structure) at varying Ded1p concentrations.
See also Figure S3.