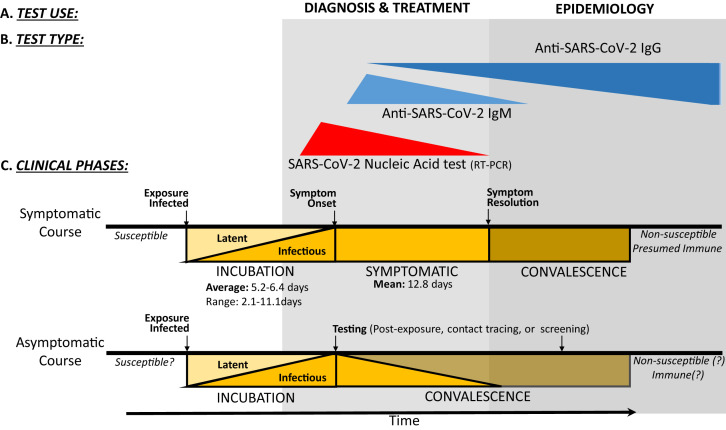
Fig 2.
COVID-19 testing uses and modalities by clinical phase: Diagnosis, treatment, infection control, and epidemiologic monitoring (A) are reliant on the thoughtful deployment and use of various clinical testing modalities (B), including NAT (primarily implemented via RT-PCR) and anti–SARS-CoV-2 serology (IgM and IgG). Each testing modality has maximal utility at a given clinical phase (C), with NATs being most useful during late incubation and symptomatic illness and serology being useful during resolution of illness/convalescence. Classically, antiviral IgM antibodies develop early in an acute infection before IgG antibodies, but recent reports suggest that IgM and IgG seroconversion occurs simultaneously in many subjects during the second week of infection. The persistence of protective humoral IgG-mediated immunity is not yet established for COVID-19 survivors. The natural history of asymptomatic carriers of SARS-CoV-2 is also not yet clear.13, 14, 15, 16