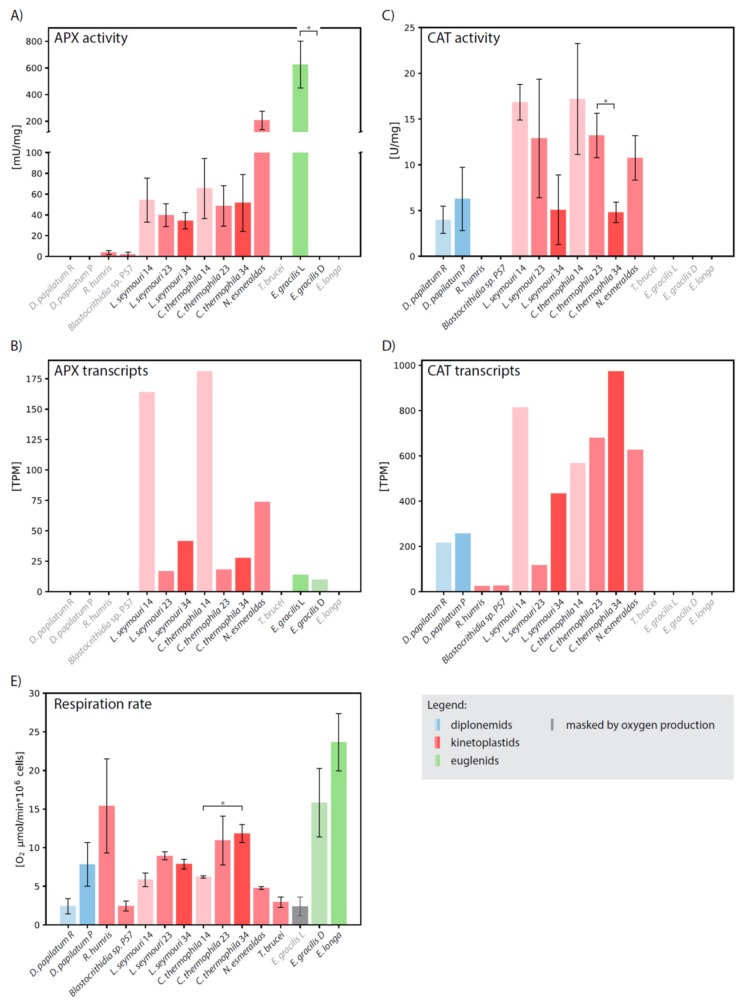
Figure 3.
Biochemical and transcriptomic analysis. Comparison of (A) APX and (C) CAT activities, (B) APX and (D) CAT expression levels, and (E) oxygen uptake in Diplonema papillatum cultivated in nutrient-rich (R) and nutrient-poor (P) medium, Rhynchopus humris, Blastocrithidia sp. P57, Leptomonas seymouri cultivated at 14 °C (14), 23 °C (23) and 34 °C (34), Crithidia thermophila cultivated at 14 °C (14), 23 °C (23) and 34 °C (34), Novymonas esmeraldas, Trypanosoma brucei, Euglena gracilis cultivated in light (L) and dark (D), and Euglena longa. Species names in grey denote organisms, in which corresponding enzyme was not identified. Activity U is defined as the amount of the enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of 1 μmol of ascorbate (APX) or H2O2 (CAT) per 1 min. Each experiment was performed in two biological replicates. Statistical significance of differences between organisms was evaluated by an unpaired t-test. * statistically significant (p < 0.05). Note that respiration value in light-grown E. gracilis is masked by photosynthetic oxygen consumption (grey bar).