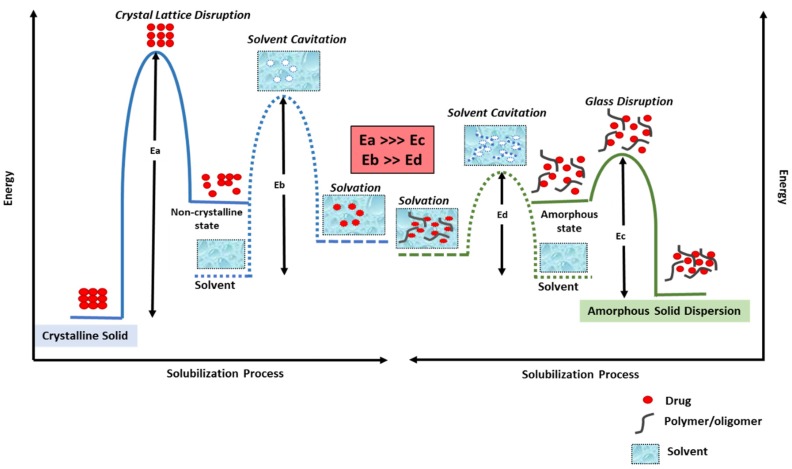
Figure 2.
Activation energy diagram for the solubilization of a drug from a crystalline form (right) and from an ASD (left). (Ea is the energy required to disrupt crystalline lattice of a drug in a conventional formulation; Ec is the energy required to disrupt the glass solution of a drug in an ASD formulation, Eb is the energy required for solvent cavitation in the solubilization of a crystalline solid and Ed is the energy required for solvent cavitation in the case of ASD solubilization.).