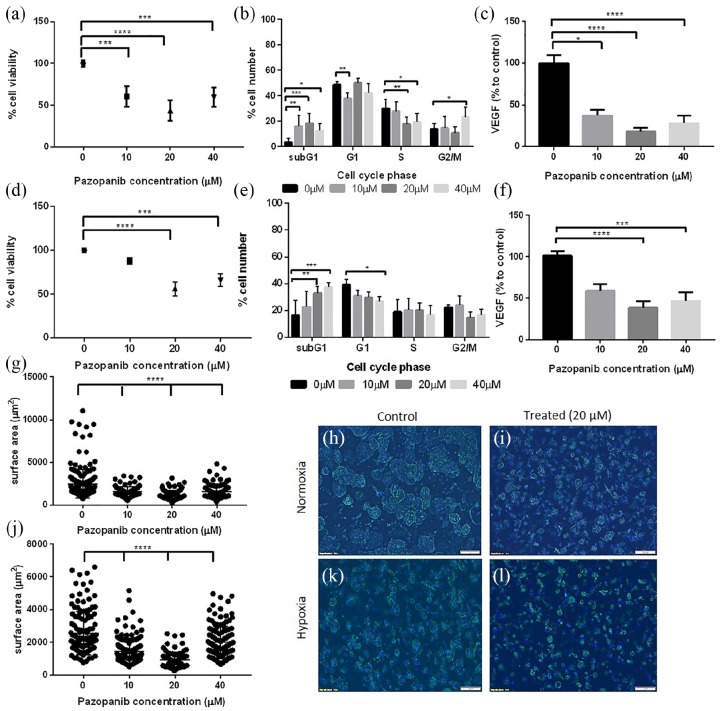
Figure 4.
Mature tumouroids manufactured using 786-O cells, treated with Pazopanib. Tumouroids were exposed to Pazopanib at day 10 of manufacture, in normoxia or hypoxia, for a total of 120 h. Normoxia (20% O2): a, b, c, g, h, i; hypoxia (1% O2): d, e, f, j, k, l. (a) Cell viability measured using CellTiter Glo after treatment with Pazopanib (normoxic conditions). (b) Cell cycle analysis of treated tumouroids (normoxic conditions). (c) VEGF levels in treated tumouroids measured using ELISA, shown as a percentage to untreated tumouroids (normoxic conditions). (d) Cell viability measured using CellTiter Glo after treatment with Pazopanib in hypoxia (1% O2). (e) Cell cycle analysis of treated tumouroids (hypoxic conditions). (f) VEGF levels in the supernatant of treated tumouroids shown as a percentage to untreated tumouroid (ELISA, hypoxic conditions). (g, j) Surface area of spheroids following treatment in (g) normoxia or (j) hypoxia demonstrating effect of treatment on spheroid size. (h, i, k, l) Fluorescent images of cancer spheroids within mature tumouroids for (h, k) control and (i, l) treated tumouroids in (h, i) normoxia or (k, l) hypoxia (Phalloidin staining, DAPI counterstain; scale bar = 100 µm).
**p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001, Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc analysis.