Fig. 5. L-TGF-β is flexible when bound to αvβ8.
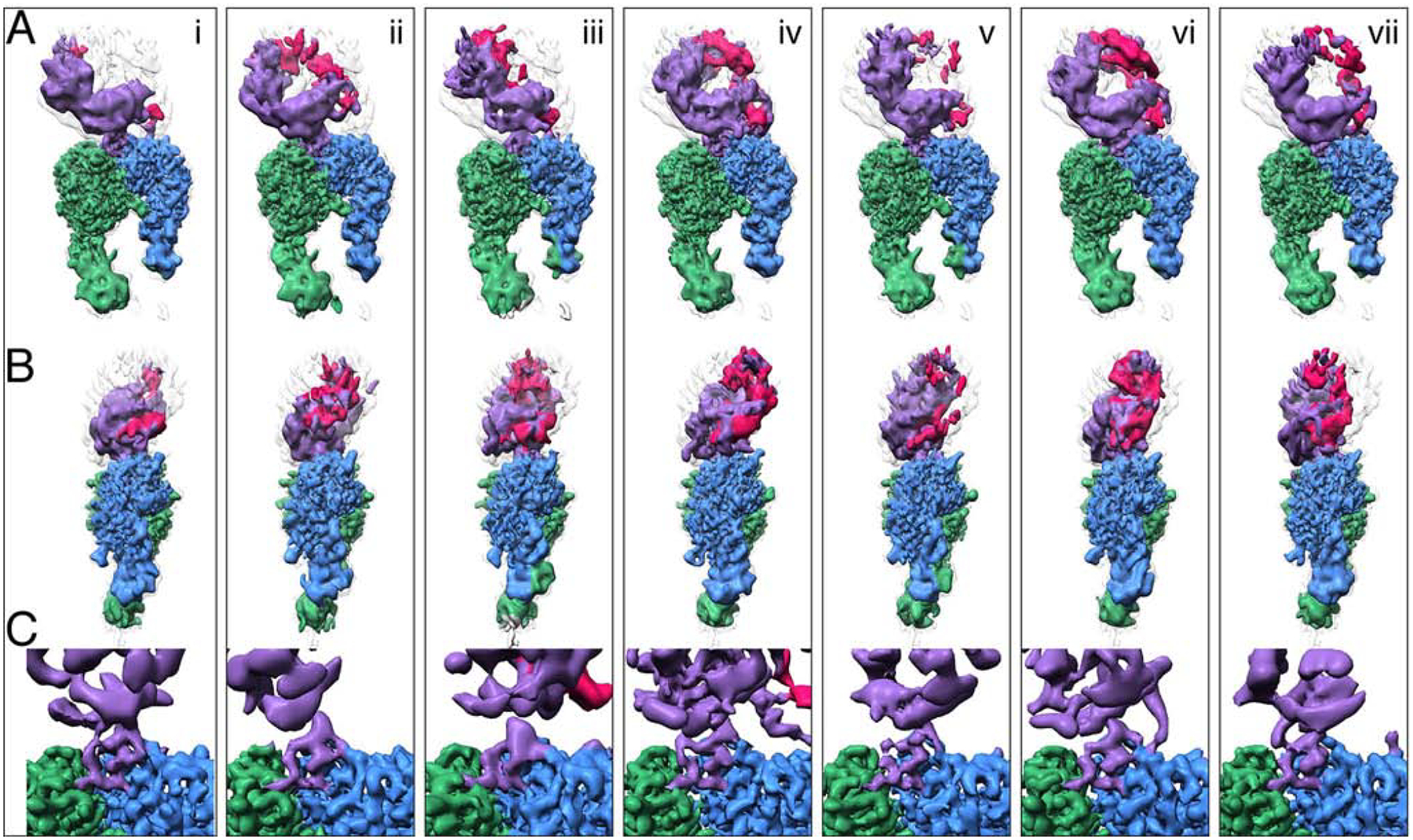
Seven structures (i-vii) illustrate the conformational variability of the αvβ8/LTGFβ complex. All structures are aligned to each other using the αv-subunit b-propeller domain. Each vertical panel shows two views (A, and B) of the same structure rotated 90˚ around the z-axis and a close-up of the integrin-ligand binding interface with the L-TGF-β integrin-binding helix (C), which is formed in all structures. Subclass (iv) is shown in Figs. 1, 2 and 4. Color coding is the same as for Fig. 2. For (A-B) the primary conformation is shown in colors, as defined in Fig. 1A, and all six other conformations are shown as semi-transparent to provide a reference for L-TGF-β’s range of motion. From left to right, the percentage of particles that went into each class are as follows: 14%, 14%, 14%, 19%, 16%, 11%, 12%. Related information is in Fig. S5.
